- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Biology復習筆記16.1.4 Identifying the Stages of Meiosis
Identifying the Stages of Meiosis
- Cells undergoing?meiosis?can be observed and photographed using specialised microscopes
- The different stages of meiosis have distinctive characteristics meaning they can be identified from photomicrographs or diagrams
Meiosis I or Meiosis II
- Homologous chromosomes?pair up side by side in meiosis I only
- This means if there are?pairs of chromosomes?in a diagram or photomicrograph?meiosis I?must be occurring
- The number of cells forming can help distinguish between meiosis I and II
- If there are?two new cells?forming it is?meiosis I?but if there are?four new cells?forming it is?meiosis II
The distinguishing features at each stage of Meiosis I
- Prophase I:?Homologous pairs?of chromosomes are visible
- Metaphase I: Homologous pairs are lined up?side by side?along the?equator?of spindle
- Anaphase I:?Whole chromosomes?are being pulled to opposite?poles?with?centromeres intact
- Telophase I: There are?2 groups?of condensed chromosomes around which nuclei membranes are forming
- Cytokinesis: Cytoplasm is dividing and?cell membrane is pinching inwards?to form?two cells
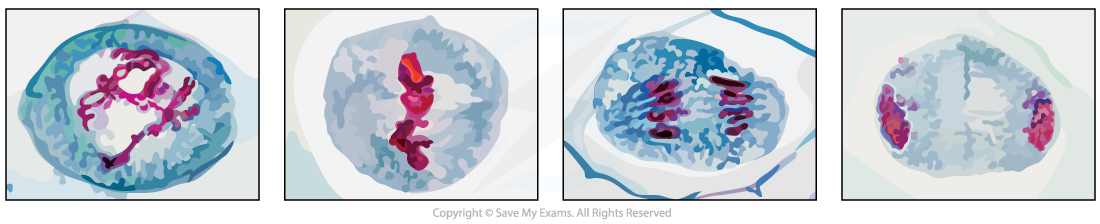
The distinguishing features at each stage of Meiosis II
- Prophase II:?Single whole chromosomes?are visible
- Metaphase II: Single whole chromosomes are lined up along the?equator?of the spindle in?single file?(at 90 degree angle to the old spindle)
- Anaphase II:?Centromeres divide?and?chromatids?are being pulled to opposite?poles
- Telophase II: Nuclei are forming around the?4 groups?of condensed chromosomes
- Cytokinesis: Cytoplasm is dividing and?four haploid cells?are forming
Identifying the stages of meiosis table
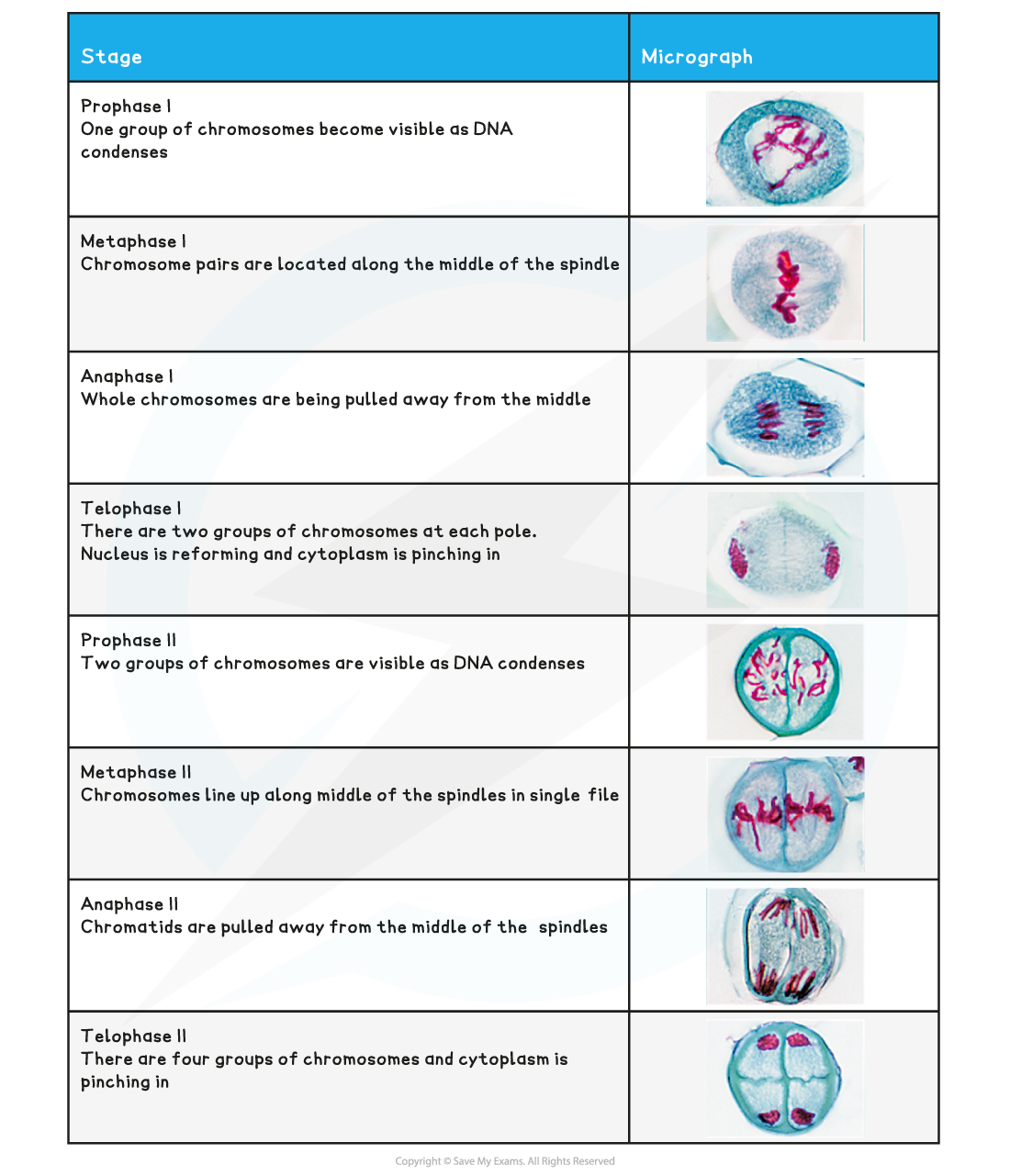
Prophase I, Metaphase I , Anaphase I and Telophase I as seen in photomicrographs
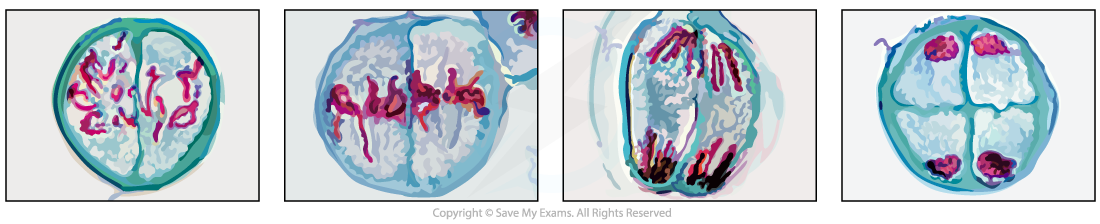
Prophase II, Metaphase II , Anaphase II and Telophase II as seen in photomicrographs
Exam Tip
For metaphase remember?M for the middle?of the spindle and cell which is where the chromosomes will be lined up.For anaphase remember?A for away?from the middle to the poles, which is where the chromosomes / chromatids are being pulled.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









