- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics復習筆記2.3.2 The Electromagnetic & Strong Force
The Electromagnetic Force
- The electromagnetic force is only between charged particles
- The exchange particle that carries this force is the?virtual photon, γ
- Properties of the photon are:
- It has no mass
- It has no charge
- It is its own antiparticle
- Electromagnetic interactions occur whenever two charged particles interact with each other
- For example, when two charged particles, such as electrons, are repelled by each other, a virtual photon is exchanged between them to produce this repulsion
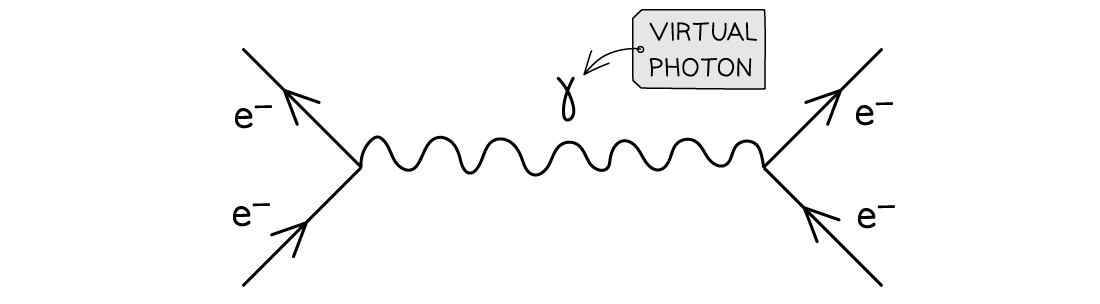
Feynman diagram of electromagnetic repulsion between two electrons shown by the exchange of a virtual photon
- The electromagnetic force is also responsible for binding electrons to atoms
- This is due to the attractive force between the negative electrons and positive nucleus
Hadrons & The Strong Nuclear Force
- Hadrons are particles that are made up of quarks
- Hence they are subject to the?strong?interaction
- The exchange particle of the strong interaction is either:
- The?pion?(between nucleons)
- The?gluon?(between quarks)
- This means that?leptons?cannot interact with the strong force, since they are not made up of quarks

Feynman diagram of the interaction between an up and down quark. The gluon is the exchange particle between them.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









