- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY: DOUBLE SCIENCE 復習筆記:4.4.1 Alkenes
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY: DOUBLE SCIENCE 復習筆記:4.4.1 Alkenes
The Alkenes
- All alkenes contain a?double carbon bond, which is shown as two lines between two of the carbon atoms i.e. C=C
- All alkenes contain a double carbon bond, which is the?functional group?and is what allows alkenes to react in ways that alkanes cannot
- The names and structure of the first four alkenes are shown below:
Table Showing the Formulae and Structures of the First Four Alkenes
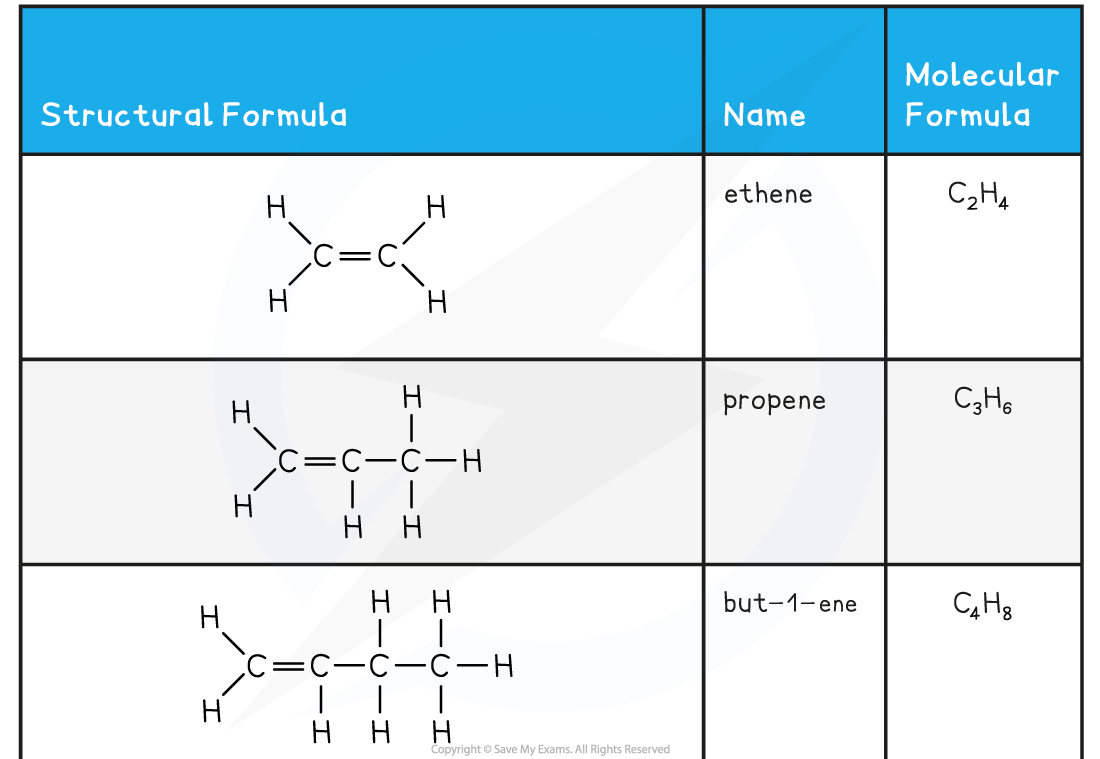
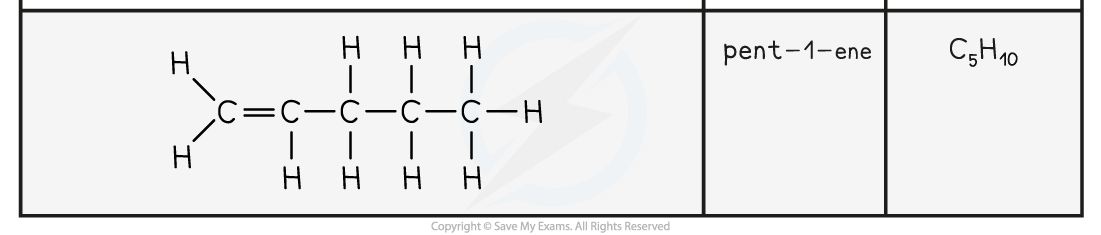
- Compounds that have a C=C double bond are also called unsaturated compounds
- That means they can?make more bonds?with other atoms by opening up the C=C bond and allowing incoming atoms to form another single bond with each carbon atom of the functional group
- Each of these carbon atoms now forms 4 single bonds instead of 1 double and 2 single bonds
- This makes them much more reactive than alkanes

A carbon-carbon double can break and form a single bond, allowing more atoms to attach to the carbon atoms
Exam Tip
The numbers in butene, pentene and hexene refer to the carbon atom in which the C=C begins, counting from the left. E.g. pent-2-ene, C5H10?has the C=C between the 2nd?and 3rd?carbon atoms. In pent-3-ene the C=C bond is between the 3rd?and 4th?carbon atoms from the left.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









