- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY: DOUBLE SCIENCE 復習筆記:1.2.4 Interpreting Chromatograms
EDEXCEL IGCSE CHEMISTRY: DOUBLE SCIENCE 復習筆記:1.2.4 Interpreting Chromatograms
Identifying Mixtures
- Pure substances will produce only?one spot?on the chromatogram
- If two or more substances are the same, they will produce identical chromatograms
- If the substance is a?mixture, it will separate on the paper to show all the?different?components?as?separate?spots
- An impure substance therefore will produce a chromatogram with more than one spot
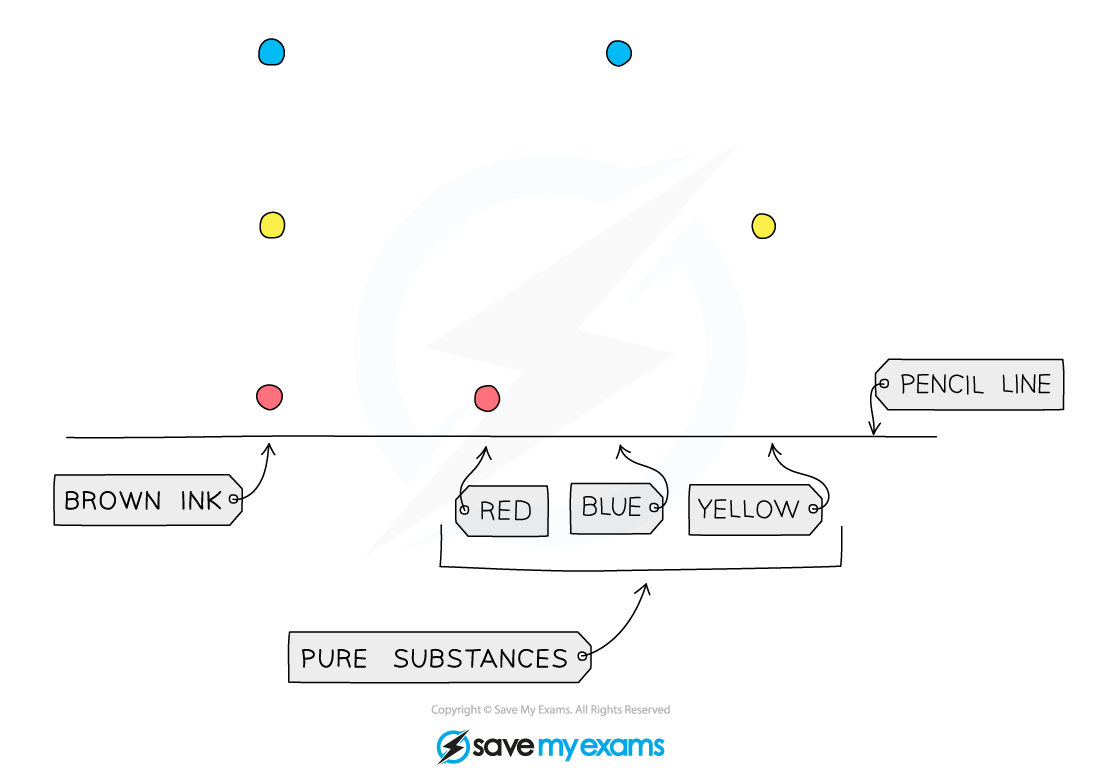
Diagram showing the analysis of a mixture and pure substances using chromatography
Rf Values
- These values are used to?identify?the components of mixtures
- The?Rf?value of a particular compound is always the?same?but it is dependent, however, on the solvent used
- If the solvent is changed then the value changes
- Calculating the?Rf?value allows chemists to?identify unknown substances?because it can be compared with?Rf?values of known substances under the same conditions
- These values are known as?reference values
Calculation
- The Retention factor is found using the following calculation:
Rf = distance travelled by substance ÷ distance travelled by solvent
- The Rf value will always lie between 0 and 1; the closer it is to 1, the more soluble is that component in the solvent
- The?Rf?value is a ratio and therefore has no units
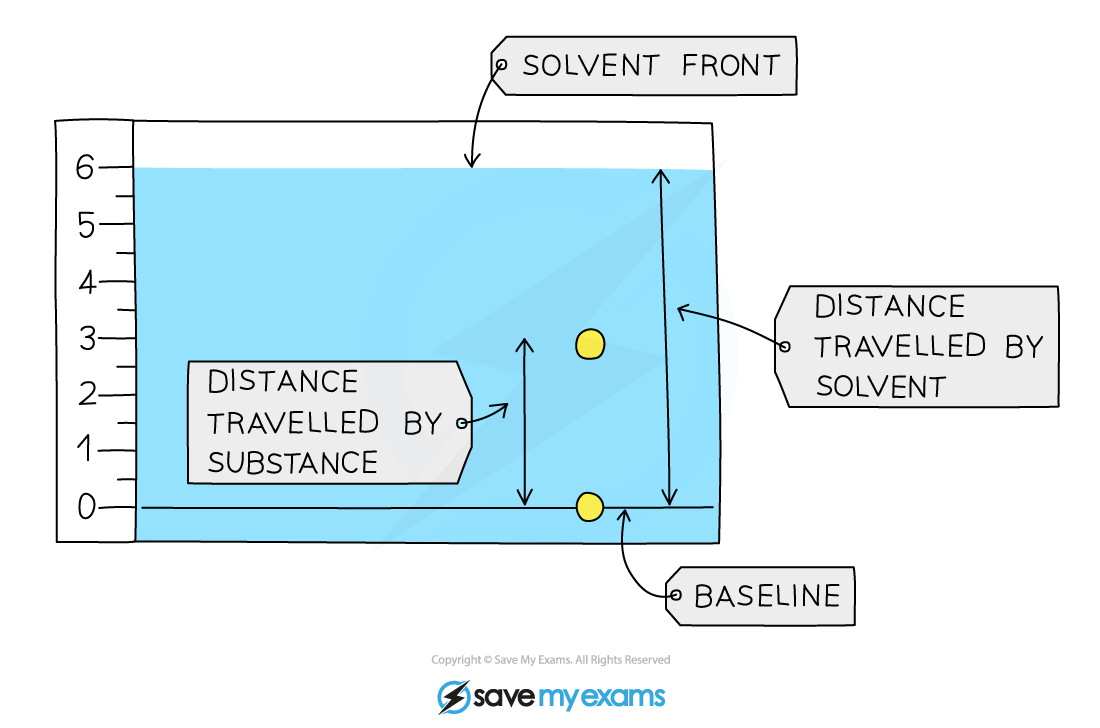
Using Rf?values to identify components of a mixture
Exam Tip
For the Rf?calculations, both distances are measured from the baseline.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









