- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Double Science 復習筆記:7.1.3 Types of Radiation
Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Double Science 復習筆記:7.1.3 Types of Radiation
Types of Radiation
Unstable Nuclei and Radiation
- Some atomic nuclei are?unstable
- This is because of an imbalance in the forces within the nucleus
- Forces exist between the particles in the nucleus
- Carbon-14 is an?isotope?of carbon which is unstable
- It has two extra neutrons compared to stable carbon-12

Carbon-12 is stable, whereas carbon-14 is unstable. This is because carbon-14 has two extra neutrons
- Some isotopes are unstable because of their large size or because they have too many or too few neutrons
- Unstable nuclei can emit?radiation?to become more stable
-
- Radiation can be in the form of a high energy particle or wave

Unstable nuclei decay by emitting high energy particles or waves
- As the radiation moves away from the nucleus, it takes some energy with it
- This reduces the overall energy of the nucleus
- This makes the nucleus more?stable
- The process of emitting radiation is called?radioactive decay
- Radioactive decay is a?random?process
- This means it is not possible to know exactly when a particular nucleus will decay
- When an unstable nucleus decays it emits radiation, called?nuclear radiation
- There are different types of radiation that can be emitted:
- Alpha (α)
- Beta (β-)
- Gamma (γ)
Worked Example
Which of the following statements is?not?true?
A? ? Isotopes can be unstable because they have too many or too few neutrons
B? ? The process of emitting particles or waves of energy from an unstable nucleus is called radioactive decay
C? ? Scientists can predict when a nucleus will decay
D? ? Radiation refers to the particles or waves emitted from a decaying nucleus
ANSWER:? C
-
- Answer A is?true.?The number of neutrons in a nucleus determines the stability
- Answer B is?true.?This is a suitable description of radioactive decay
- Answer D is?true.?Radiation is about emissions. It is different to radioactive particles
- Answer C is?not true
- Radioactive decay is a random process
- It is not possible to predict precisely when a particular nucleus will decay
Exam Tip
The terms?unstable,?random?and?decay?have very particular meanings in this topic. Remember to use them correctly when answering questions!
Properties of Radiation
- The three different forms of nuclear radiation have different properties:
Alpha Particles
- The symbol for alpha is?α
- An alpha particle is the same as a helium nucleus
- This is because they consist of two neutrons and two protons
- Alpha particles have a charge of +2
- This means they can be affected by an electric field
Beta Particles
- The symbol for beta is?β-
- Beta particles are fast-moving electrons
- They are produced in nuclei when a neutron changes into a proton and an electron
- Beta particles have a charge of -1
- This means they can be affected by an electric field
Gamma Rays
- The symbol for gamma is?γ
- Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves
- They have the highest energy of the different types of electromagnetic waves
- Gamma rays have no charge

Alpha particles, beta particles and gamma waves can be emitted from unstable nuclei
- The properties of Alpha, Beta and Gamma are given in this table, and then described in more detail below
Different Properties of Nuclear Radiation

- The trend down the table shows:
- The range increases
- Penetrating power increases
- Ionisation decreases
Penetrating Power
- Alpha, beta and gamma have different properties
- They?penetrate?materials in different ways
- This means they are stopped by different materials

Alpha, beta and gamma are different in how they penetrate materials. Alpha is the least penetrating, and gamma is the most penetrating
- Alpha is stopped by?paper, whereas beta and gamma pass through it
- Beta is stopped by a few millimetres of aluminium
- Gamma can pass through?aluminium
- Gamma rays are only partially stopped by thick?lead
Ionising Power
- All nuclear radiation is capable of?ionising?atoms that it hits
- When an atom is ionised, the number of electrons it has changes
- This gives it a?non-zero?charge
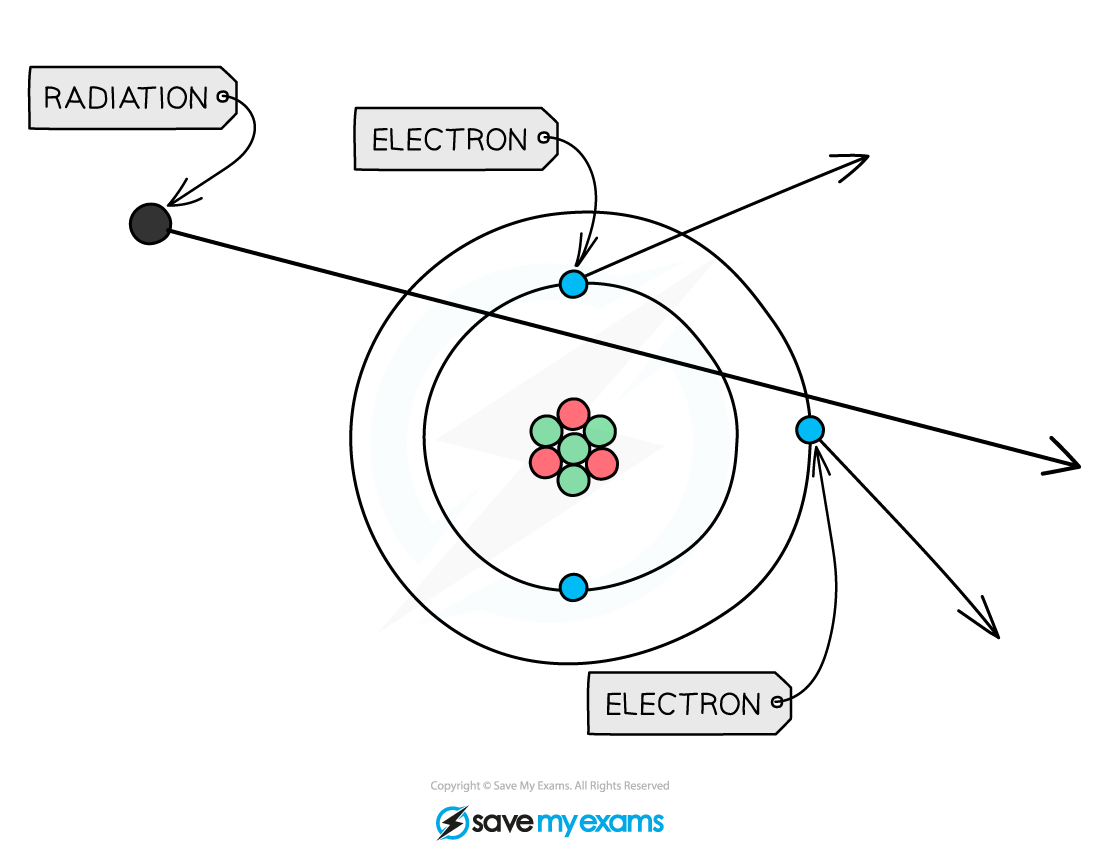
When radiation passes close to atoms it can knock out electrons, ionising the atom
- Alpha radiation is the most ionising form of nuclear radiation
- This is because alpha particles have a charge of +2
- Gamma radiation is the least ionising form of nuclear radiation
Worked Example
A student has an unknown radioactive source. They are trying to work which type of radiation is being given off:
A? ? Alpha particles
B? ? Beta particles
C? ? Gamma rays
D? ? Neutrons
They measure the count-rate, using a Geiger-Muller tube, when the source is placed behind different material. Their results are shown in the table below:
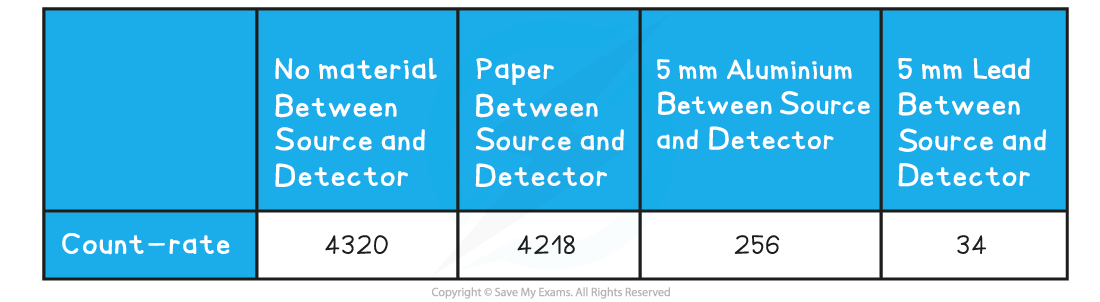
Which type of radiation is being given off by the source?
ANSWER:? B
-
- The answer is?not A?because the radiation passed through the paper almost unchanged
- This means it is?not?alpha
- The answer is?not C or D?because the aluminium decreased the count-rate significantly
- This means it is?not?gamma (gamma penetrates aluminium)
- This also means it is?not?neutrons (neutrons penetrate aluminium, however you do not need to know this for your GCSE)
- Therefore, the source must be?Beta?particles
- The answer is?not A?because the radiation passed through the paper almost unchanged
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









