- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Double Science 復習筆記:4.2.2 Gravitational Potential Energy
Edexcel IGCSE Physics: Double Science 復習筆記:4.2.2 Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational Potential Energy
- The gravitational potential energy (GPE) of an object (also known as its gravitational store) is defined as:
The energy an object has due to its height in a gravitational field
- This means:
- If an object is lifted up it will?gain?GPE
- If it falls, it will?lose?GPE
- The GPE of an object can be calculated using the equation:
GPE = mgh
- Where:
- GPE = gravitational potential energy, in Joules (J)
- m?= mass, in kilograms (kg)
- g?= gravitational field strength in Newtons per kilogram (N/kg)
- h?= height in metres (m)

The mass now has GPE as it is lifted above the ground
Gravitational Field Strength
- The gravitational field strength (g) on the?Earth?is approximately 10 N/kg
- The gravitational field strength on the surface of the?Moon?is?less?than on the Earth
- This means it would be?easier?to lift a mass on the Moon than on the Earth
- The gravitational field strength on the surface of the gas giants (eg. Jupiter and Saturn) is?more?than on the Earth
- This means it would be?harder?to lift a mass on the gas giants than on the Earth

Some values for g on the different objects in the Solar System
- The two graphs below show how GPE changes with height for a ball being thrown up in the air and when falling down

Graphs showing the linear relationship between GPE and height
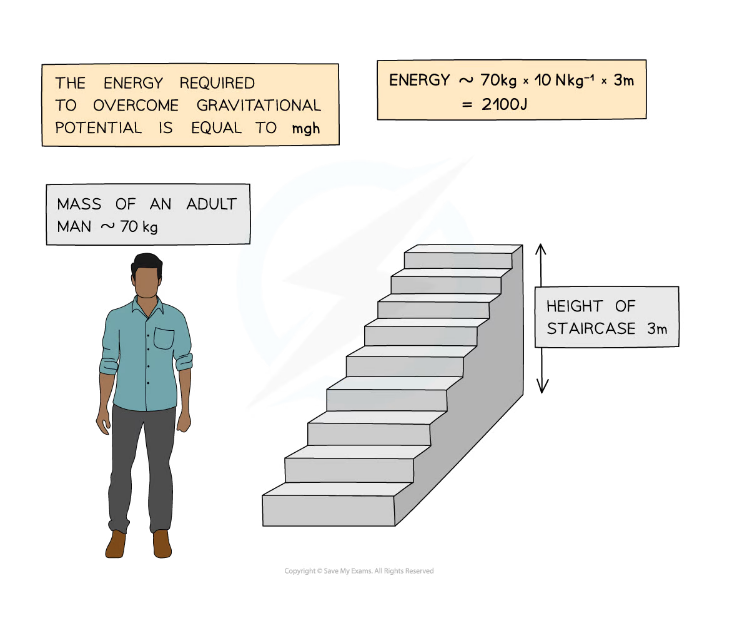
Worked Example
A man of mass 70 kg climbs a flight of stairs that is 3 m higher than the floor. Gravitational field strength is approximately 10 N/kg.Calculate the increase in his gravitational potential energy store.
Step 1: List the known quantities
-
- Mass of the man,?m?= 70 kg
- Gravitational field strength,?g?= 10 N/kg
- Height,?h?= 3 m
Step 2: Write down the equation for gravitational potential energy
GPE = mgh
Step 3: Calculate the gravitational potential energy
GPE = 70 × 10 × 3 =?2100 J
Exam Tip
When doing calculations involving gravitational field strength,?g, don't panic, you will?always?be told the value of?g?in your examination paper!
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1