- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Biology: Double Science 復習筆記 3.1.5 Sexual Reproduction in Humans
Edexcel IGCSE Biology: Double Science 復習筆記 3.1.5 Sexual Reproduction in Humans
The Male Reproductive System
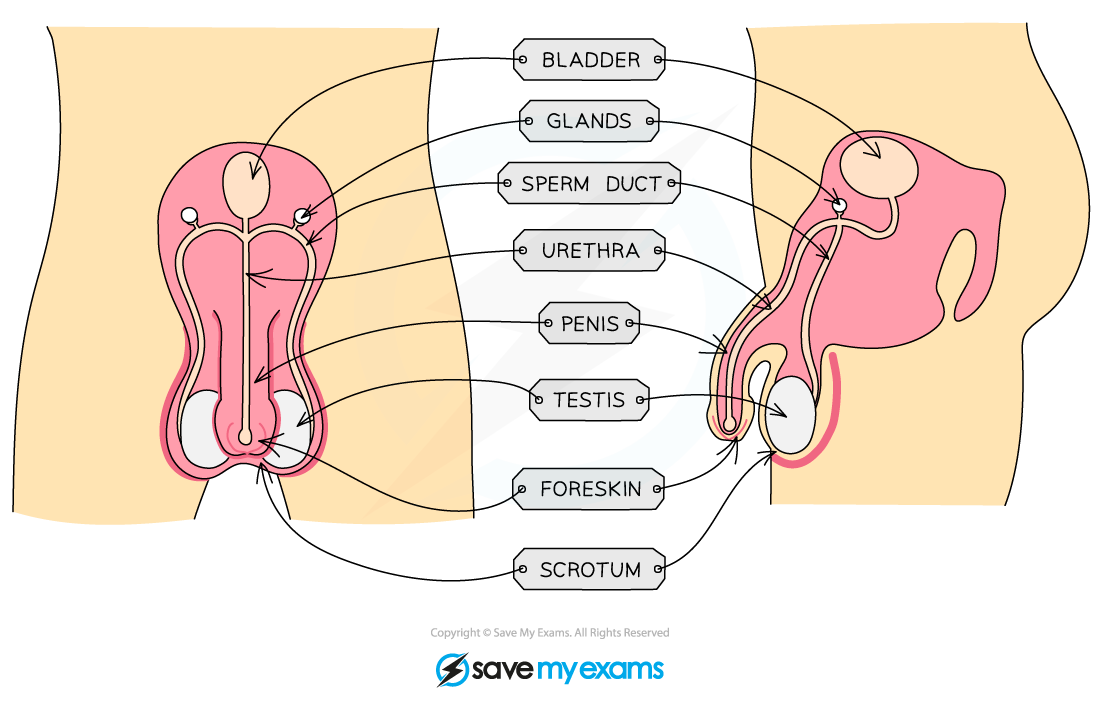
The male reproductive system
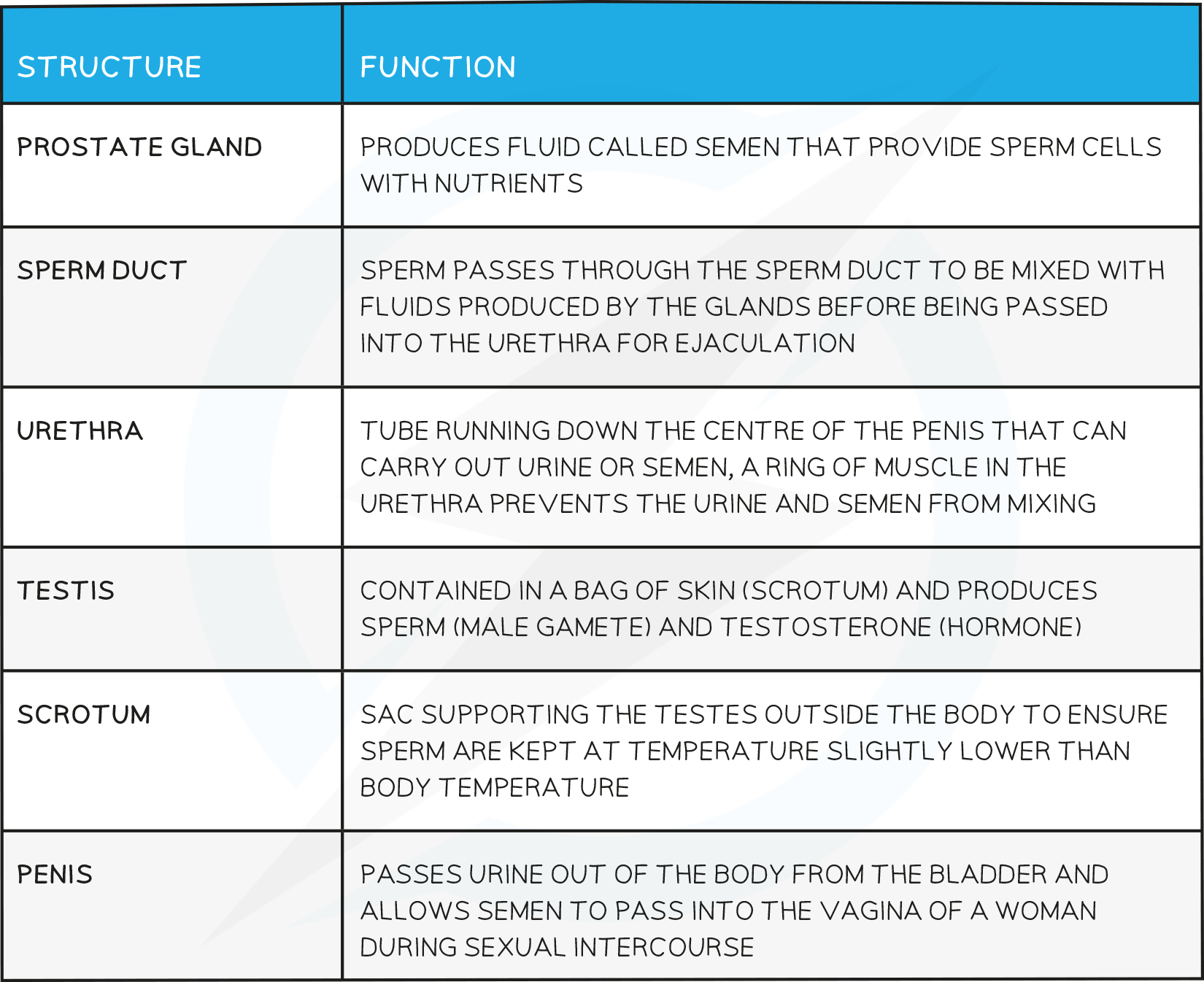
Male Reproductive Structures & their Function Table
The Female Reproductive System
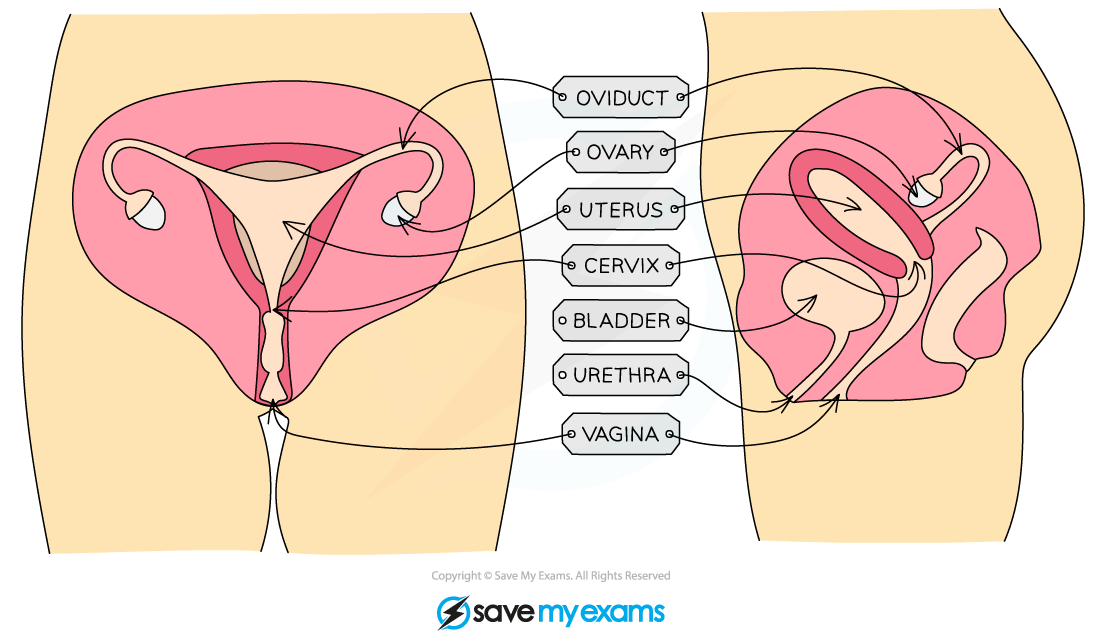
The female reproductive system
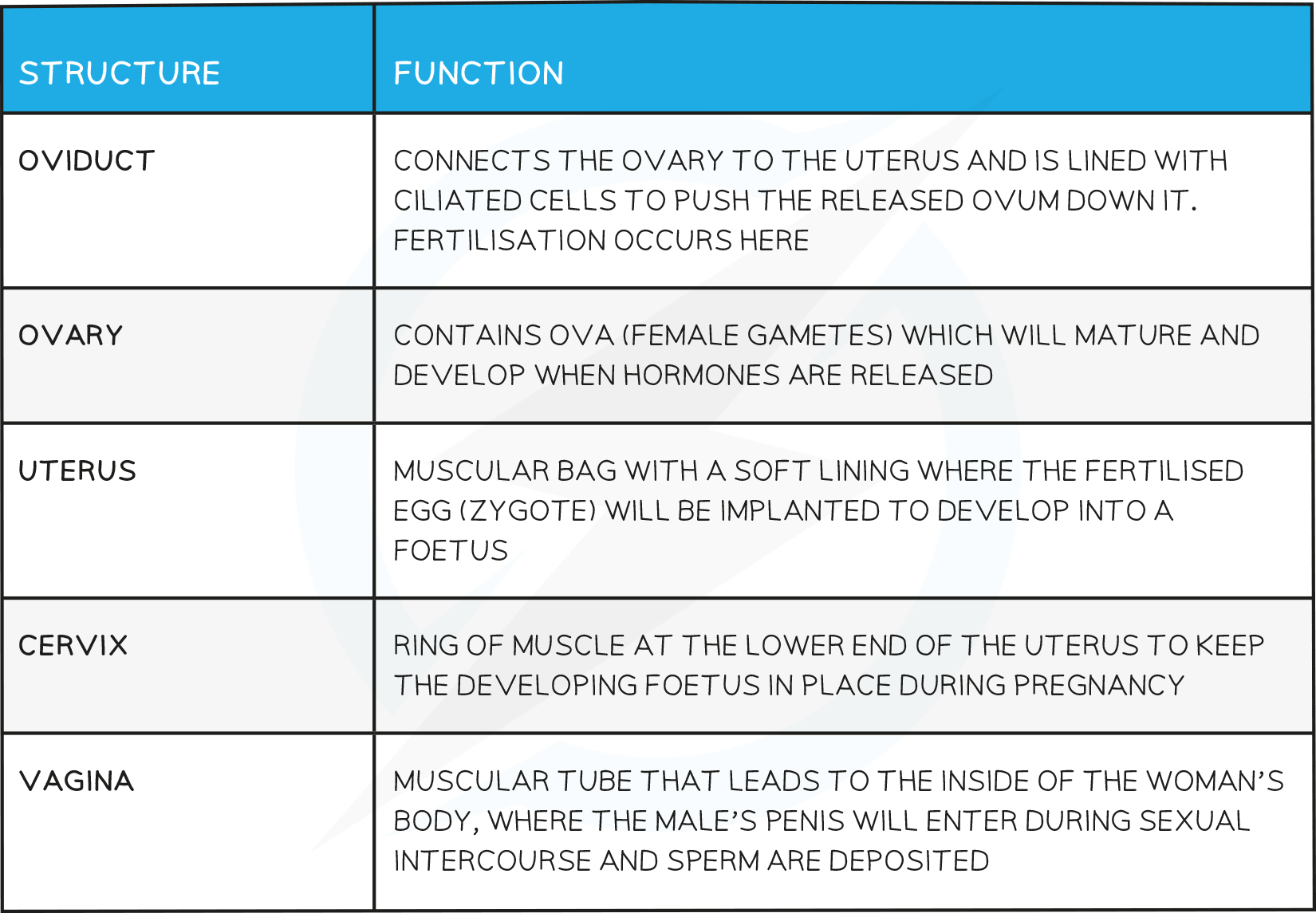
Female Reproductive Structures & their Function Table
The Gametes
- A gamete is a?sex cell?(in animals: sperm and ovum; in plants pollen nucleus and ovum) produce by meiosis
- Gametes differ from normal cells as they contain?half the number of chromosomes?found in other body cells
- This is because they only contain one copy of each chromosome, rather than the two copies found in other body cells
- In human beings, a normal body cell contains 46 chromosomes but each gamete contains 23 chromosomes
- Gametes have?adaptations?to increase the chances of fertilisation and successful development of an embryo
Sperm Cell & Egg Cell Table
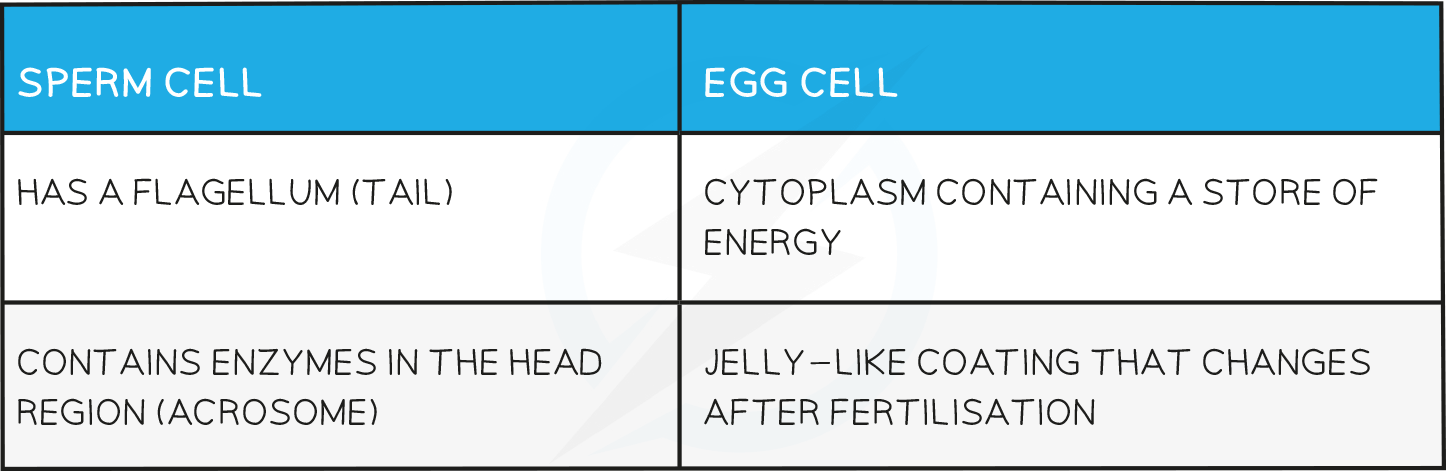
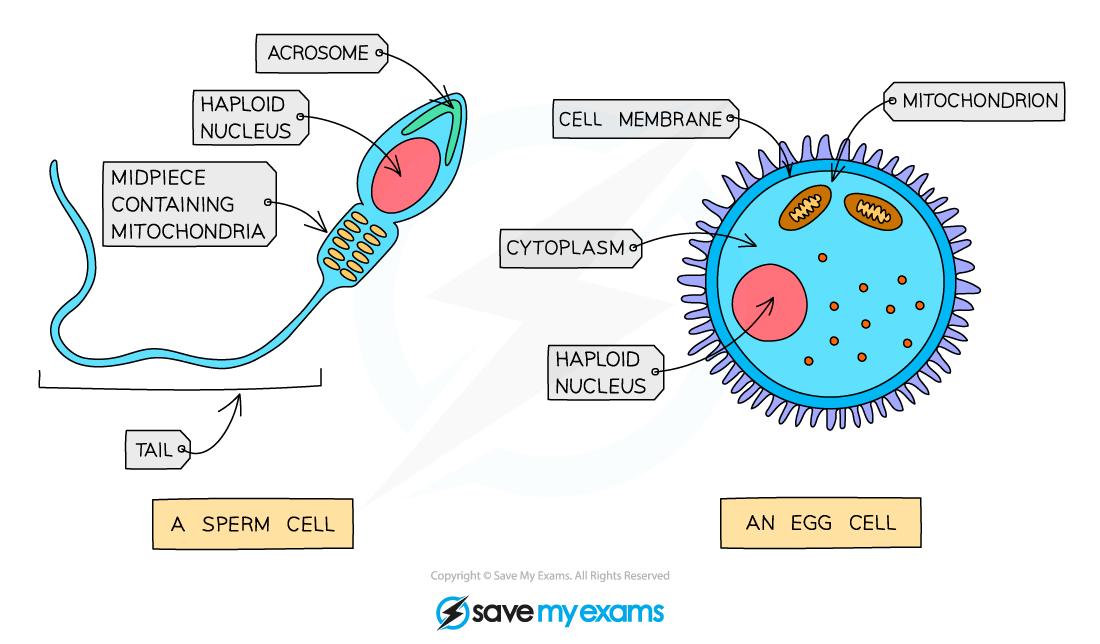
Comparing sperm and egg cells
Adaptive Features of Gametes Table
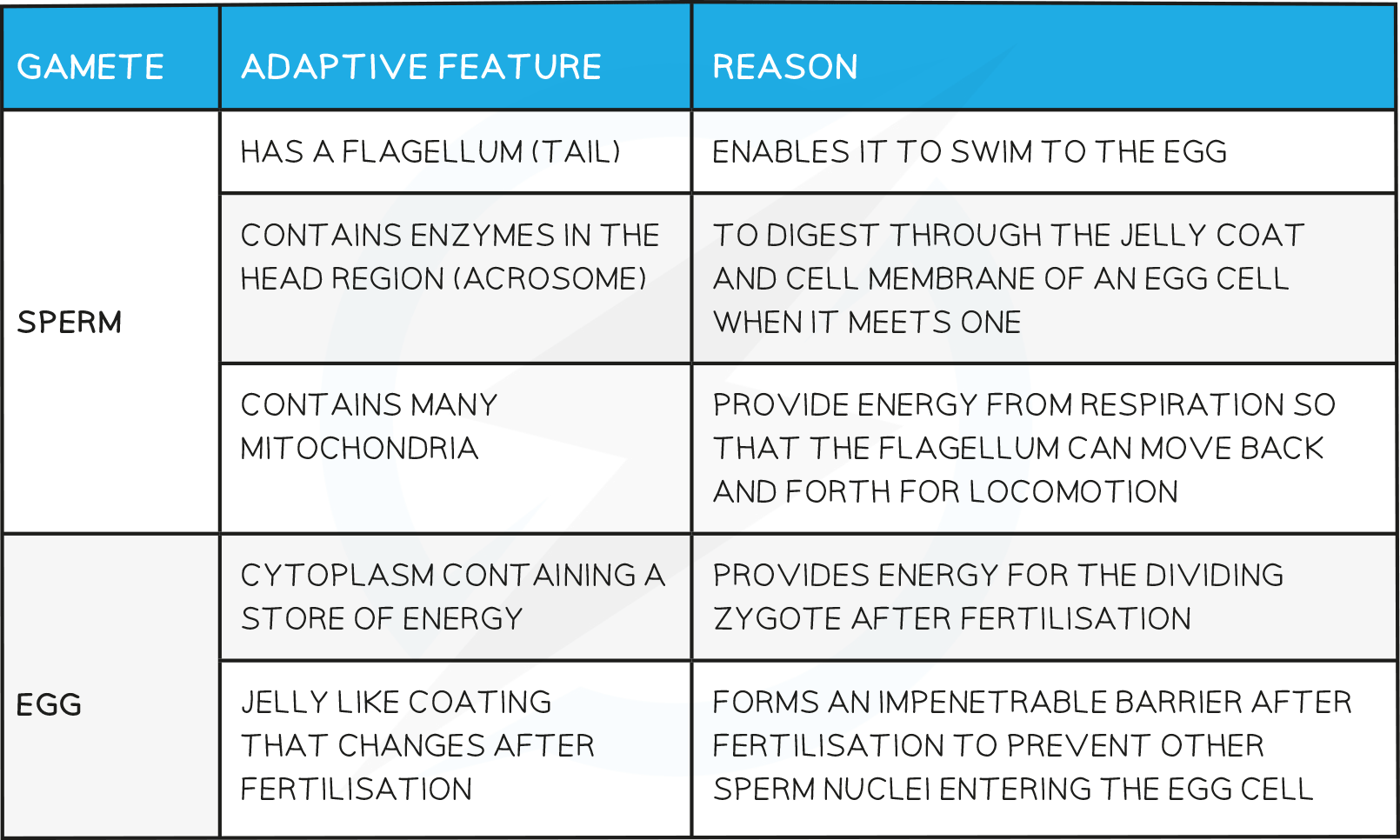
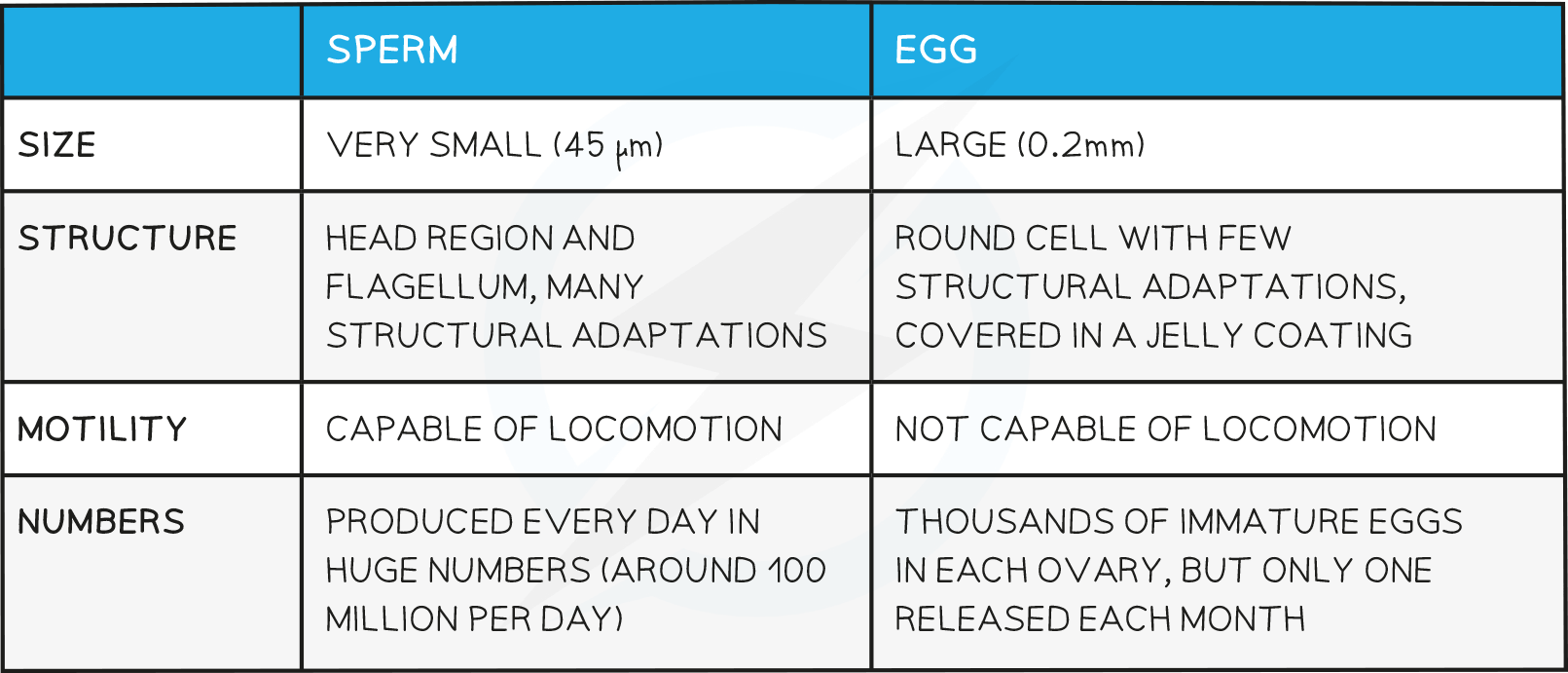
Comparison of Gametes Table
Fertilisation
- During?ejaculation?in the?male, millions of sperm cells move along the?sperm duct?(also known as the?vas deferens)
- The sperm are suspended in?semen?(a fluid secreted by the?prostate gland)
- The semen passes into the?urethra
- During sexual intercourse,?semen is ejaculated into the vagina of the female, near the cervix
- The sperm cells then follow a chemical trail and travel through the plug of mucus in the cervix to reach the?uterus?(the womb)
- The sperm cells then travel into the?oviducts
- If a sperm cell meets an egg cell in the oviduct, fertilisation can occur
- This is most likely to occur 1-2 days after the female has?ovulated?(released an egg cell from one of her ovaries into an oviduct)
- Fertilisation is the?fusion of the nuclei from a male gamete (sperm cell) and a female gamete (egg cell)
- During fertilisation, the head of a sperm cell releases enzymes that digest a path through the protective outer layer of the egg cell, allowing the sperm to pass through the egg cell membrane
- Once this occurs, the egg cell immediately releases a thick layer of material that prevents any more sperm cells from entering,?ensuring only one sperm cell can fertilise the egg cell
- When the male and female gametes fuse, they become a?zygote?(fertilised egg cell)
- This zygote contains the full?46 chromosomes?(23 pairs of chromosomes), half of which came from the father and half from the mother
- The zygote divides by?mitosis?to form two new cells, which then continue to divide like this until an?embryo?is formed after a few days
- Cell division continues and eventually many of the new cells produced become?specialised?to perform particular functions and form all the body tissues of the offspring
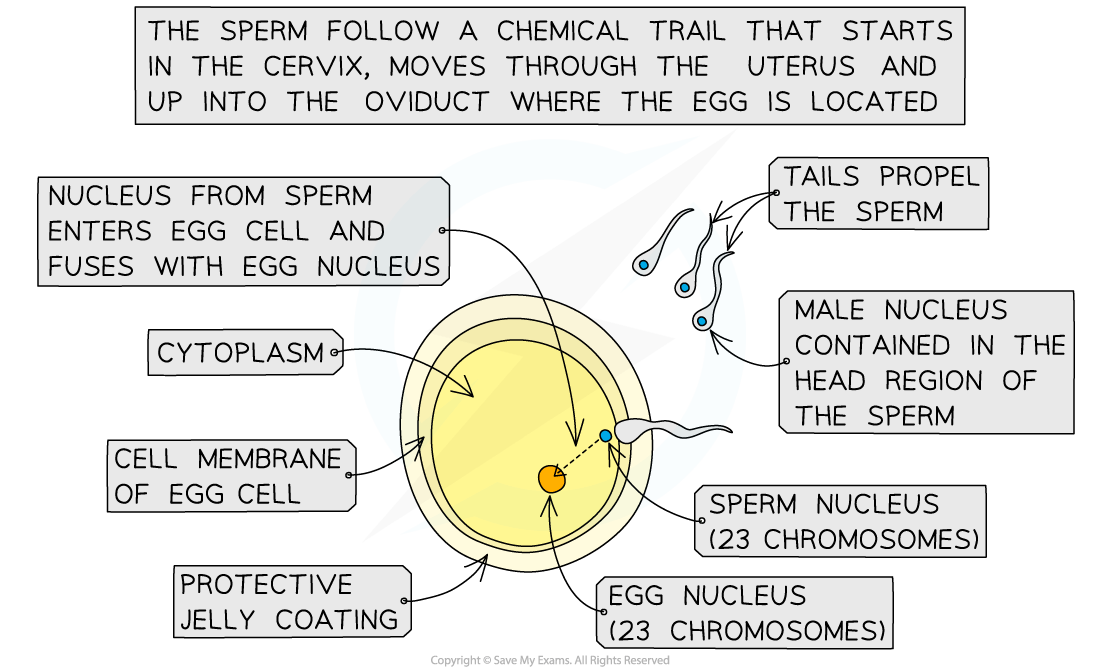
The process of fertilisation in humans
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









