- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Physics復習筆記23.2.3 Half-Life
Half-Life Definition
- Half life is defined as:
The time taken for the initial number of nuclei to reduce by half
- This means when a time equal to the half-life has passed, the activity of the sample will also half
- This is because activity is proportional to the number of undecayed nuclei, A ∝ N
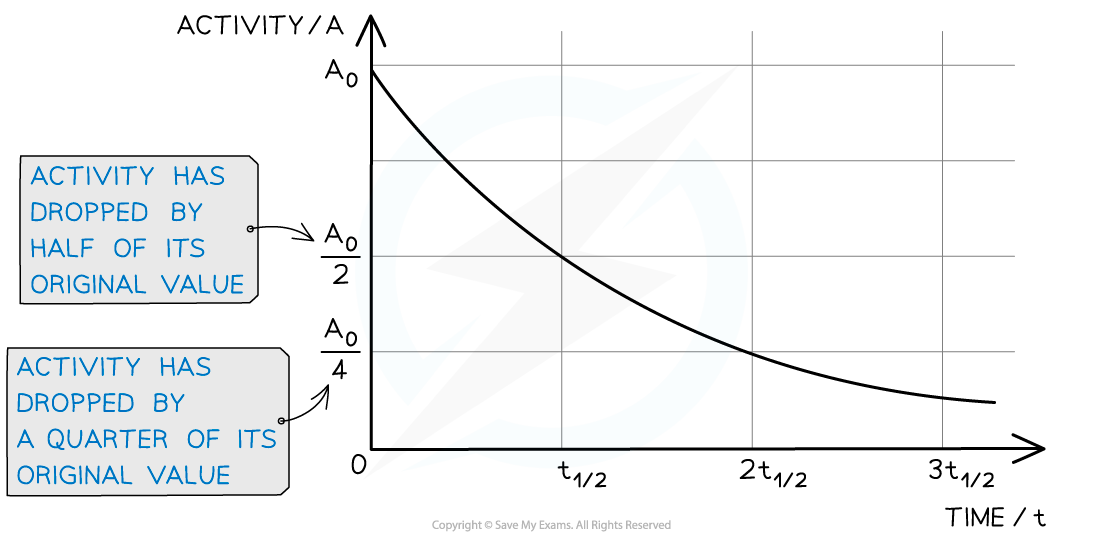
When a time equal to the half-life passes, the activity falls by half, when two half-lives pass, the activity falls by another half (which is a quarter of the initial value)
Calculating Half-Life
- To find an expression for half-life, start with the equation for?exponential decay:
N = N0e–λt
- Where:
- N = number of nuclei remaining in a sample
- N0?= the initial number of undecayed nuclei (when t = 0)
- λ = decay constant (s-1)
- t = time interval (s)
- When time t is equal to the half-life t?, the activity N of the sample will be half of its original value, so N = ? N0
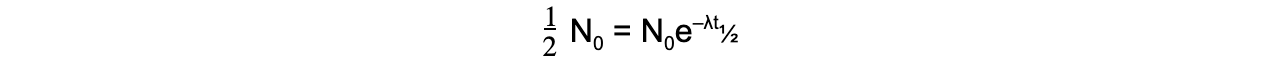
- The formula can then be derived as follows:
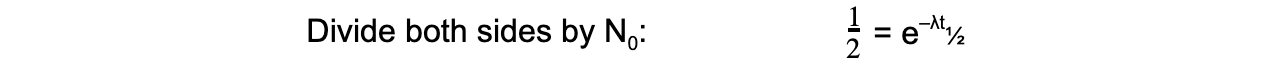


- Therefore, half-life t??can be calculated using the equation:
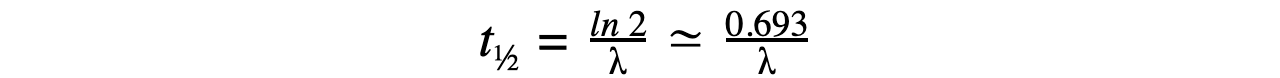
- This equation shows that half-life t??and the radioactive decay rate constant λ are inversely proportional
- Therefore, the shorter the half-life, the larger the decay constant and the?faster?the decay
Worked Example
Strontium-90 is a radioactive isotope with a half-life of 28.0 years. A sample of Strontium-90 has an activity of 6.4 × 109?Bq.Calculate the decay constant λ, in s–1, of Strontium-90.
Step 1:?Convert the half-life into seconds
28 years = 28 × 365 × 24 × 60 × 60 = 8.83 × 108?s
Step 2:?Write the equation for half-life
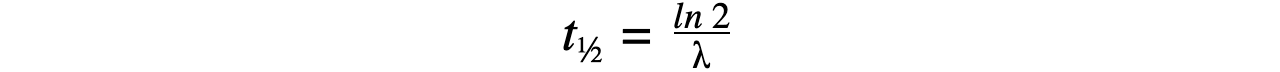
Step 3:?Rearrange for λ and calculate
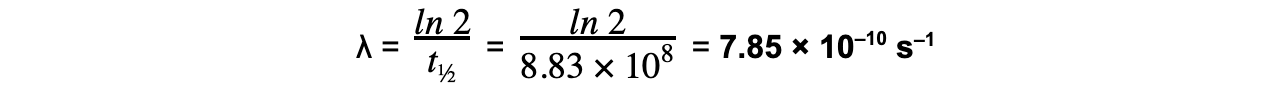
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









