- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry復(fù)習(xí)筆記7.6.1 Production of Amines
Production of Primary & Secondary Amines
- Primary amines?are organic compounds that have an -NH2?functional group attached to an alkyl or aryl group
- Secondary amines?have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to an -NH group
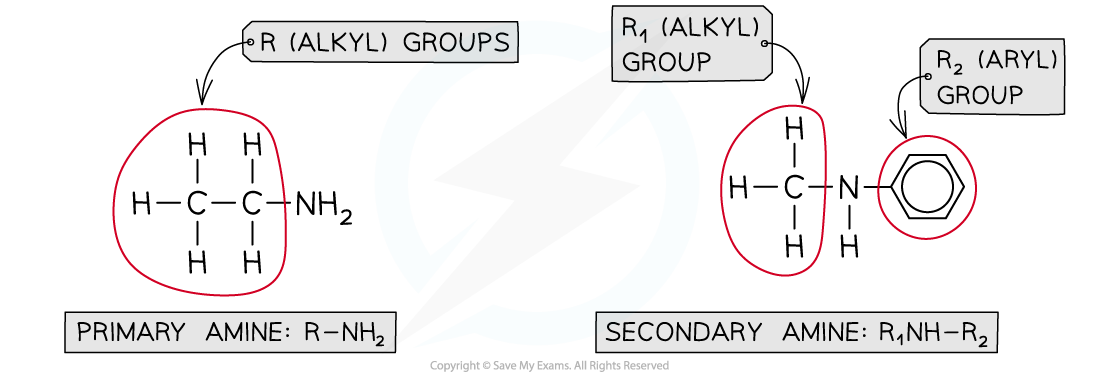 Primary and secondary amines
Primary and secondary amines
- Primary and secondary amines can be prepared from different reactions including:
- The reaction of halogenoalkanes with ammonia
- The reaction of halogenoalkanes with primary amines
- The?reduction?of amides
- The reduction of nitriles
Reaction of halogenoalkanes with ammonia
- This is a?nucleophilic substitution?reaction in which the nitrogen lone pair in ammonia acts as a?nucleophile?and?replaces?the halogen in the halogenoalkane
- When a halogenoalkane is reacted with?excess, hot ethanolic ammonia under pressure?a?primary amine?is formed

Formation of primary amine
Reaction of halogenoalkanes with primary amine
- This is also a?nucleophilic substitution?reaction in which the nitrogen in the primary amine acts as a?nucleophile?and?replaces?the halogen in the halogenoalkane
- When a halogenoalkane is reacted with a?primary amine?in?ethanol?and?heated in a sealed tube, under pressure?a?secondary amine?is formed
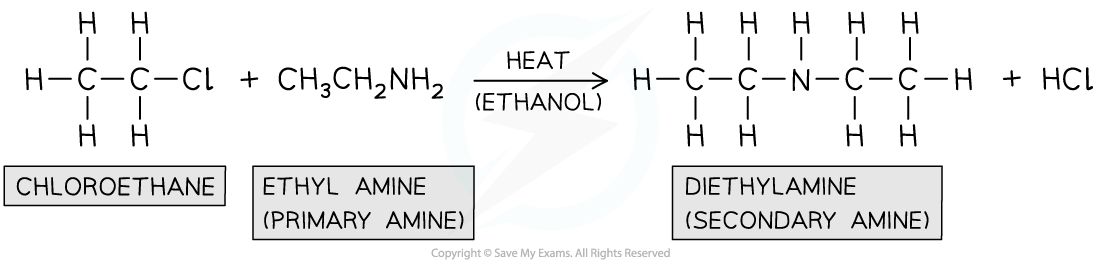
Formation of secondary amine
Reduction of amides
- Amines can also be formed from the?reduction?of?amides?by LiAlH4?in?dry ether
- Whether a primary or secondary amine is formed depends on the nature of the amide
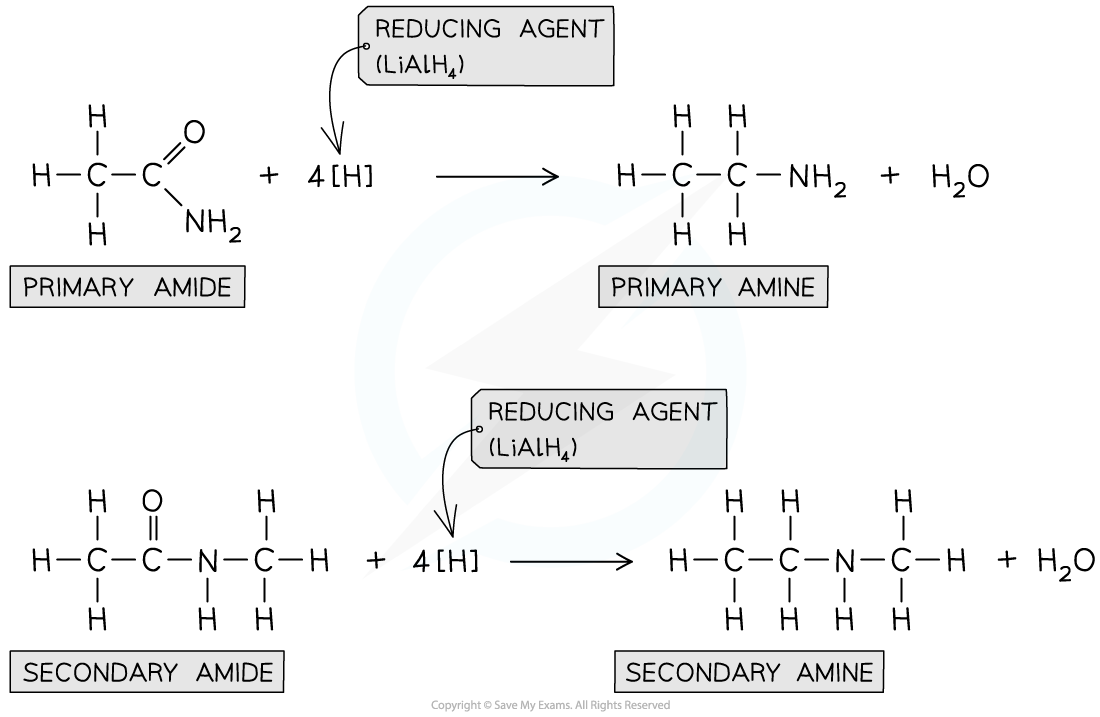
Amides can be reduced by LiAlH4?to form amines
Reduction of nitriles
- Nitriles contain a -CN functional group which can be?reduced?to an -NH2?group
- The nitrile vapour and?hydrogen gas?are passed over a?nickel catalyst?or?LiAlH4in?dry ether?can be used to form a?primary amine
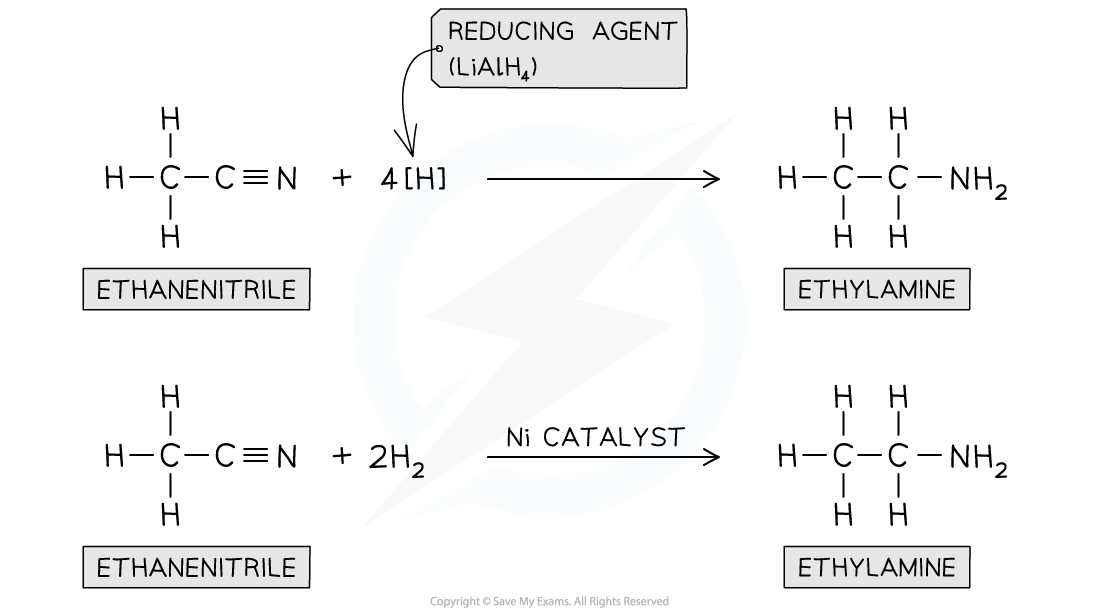
Nitriles can be reduced with LiAlH4?or H2?and Ni catalyst
轉(zhuǎn)載自savemyexams

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









