- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Chemistry復習筆記2.2.2 Reactions of Group 2 Oxides, Hydroxides & Carbonates
Reactions of Group 2 Oxides, Hydroxides & Carbonates
Reactions of Group 2 oxides with water
- All Group 2 oxides are?basic, except for BeO which is?amphoteric?(it can act both as an acid and base)
- Group 2 oxides react water to form?alkaline?solutions which get more?alkaline?going down the group
Group 2 oxide reactions with water table
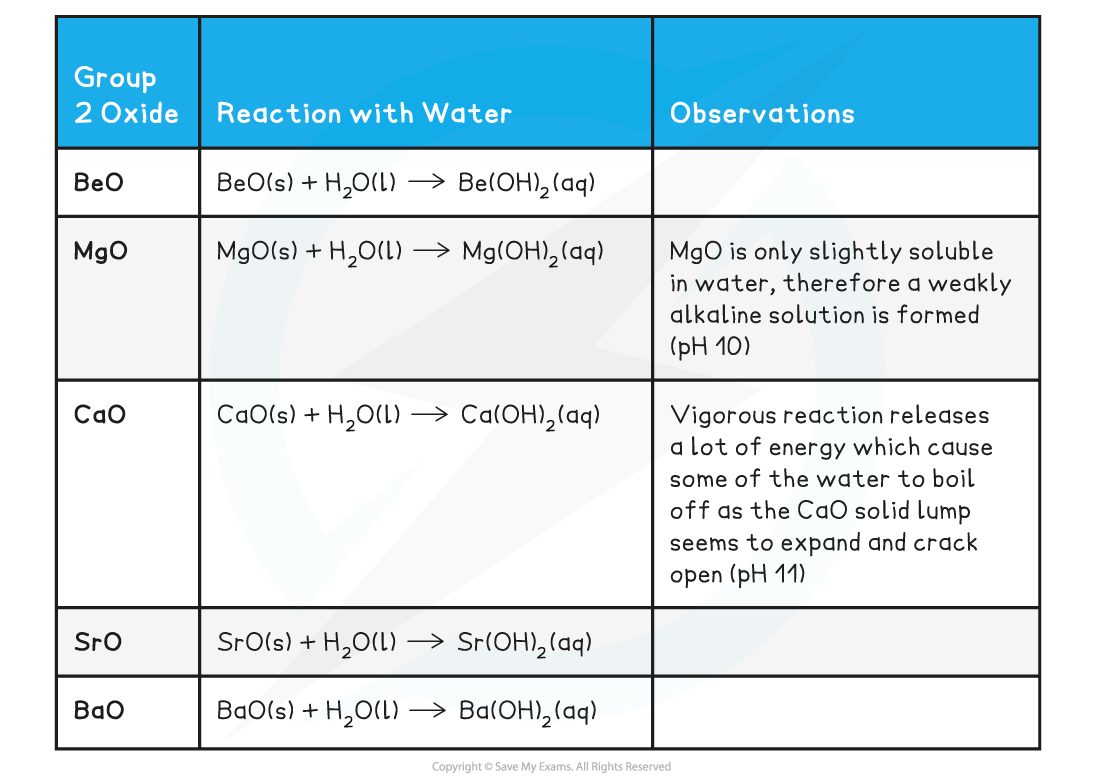
- Remember that:
oxide + water → hydroxide
And that calcium hydroxide is also called?limewater
Reactions of Group 2 metals with acid
- The Group 2 metals will react with dilute acids to form?colourless solutions of metal salts
- For example, they will form colourless solutions of metal chlorides if reacted with hydrochloric acid
- When metals react with an acid, the by-product of this reaction is hydrogen gas
Group 2 metal element reactions with dilute acids table
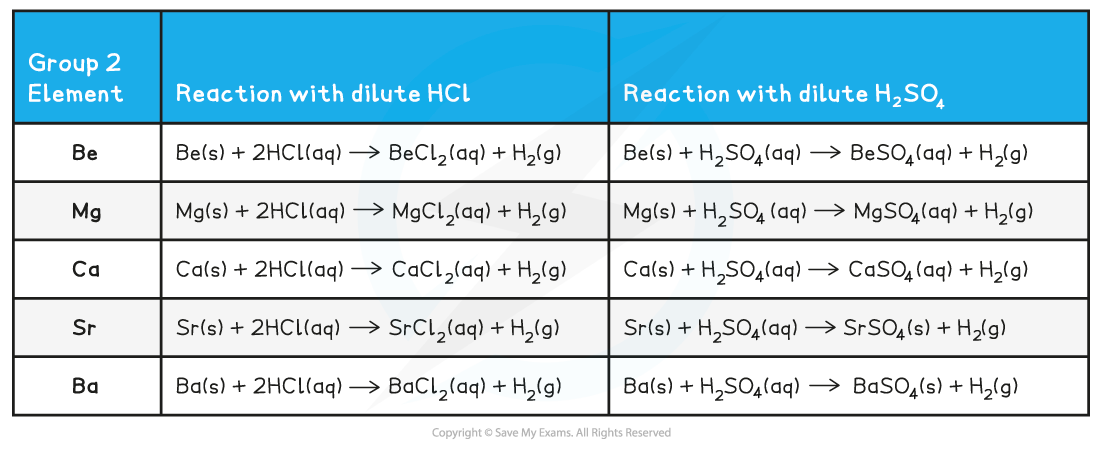
- When some of Group 2 metals react with sulfuric acid rather than hydrochloric, an insoluble sulfate forms
- Going down the group, the Group 2 sulfates become less and less soluble
- Calcium sulfate is sparingly soluble, but strontium sulfate and barium sulfate are insoluble
Reactions of Group 2 oxides with acid
- Group 2 sulfates also form when a Group 2 oxide is reacted with an acid
- The?insoluble sulfates?form at the?surface?of the oxide, which means that the solid oxide beneath it can’t react with the acid
- This can be prevented to an extent by using the oxide in?powder?form and?stirring, in which case neutralisation can take place
- Remember that:
oxide + dilute hydrochloric acid → salt + water
oxide + dilute sulfuric acid → sulfate + water
Reactions of group 2 hydroxides
- The Group 2 metal hydroxides form?colourless solutions of metal chlorides?when they react with a dilute acid
- The sulfates decrease in?solubility?going down the group (barium sulfate is an insoluble white precipitate)
Group 2 hydroxide reactions with dilute acids table
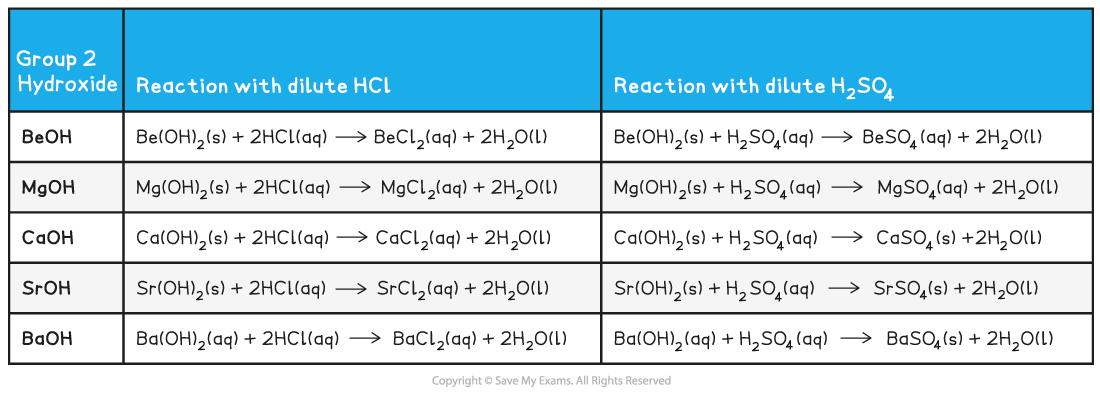
- Remember that:
hydroxide + dilute acid → salt + water
hydroxide + dilute sulfuric acid → sulfate + water
Reactions of group 2 carbonates
- All Group 2 carbonates (except for?BeCO3) are?insoluble in water
- All Group 2 carbonates will form?soluble chloride salts,?water and carbon dioxide gas when reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid
- The carbonates of Ca, Sr and Ba form as an?insoluble sulfate layer?on their solid carbonates which?stops?any further reaction after the initial bubbling (effervescence) of carbon dioxide gas?is seen
Group 2 carbonate reactions with dilute acids
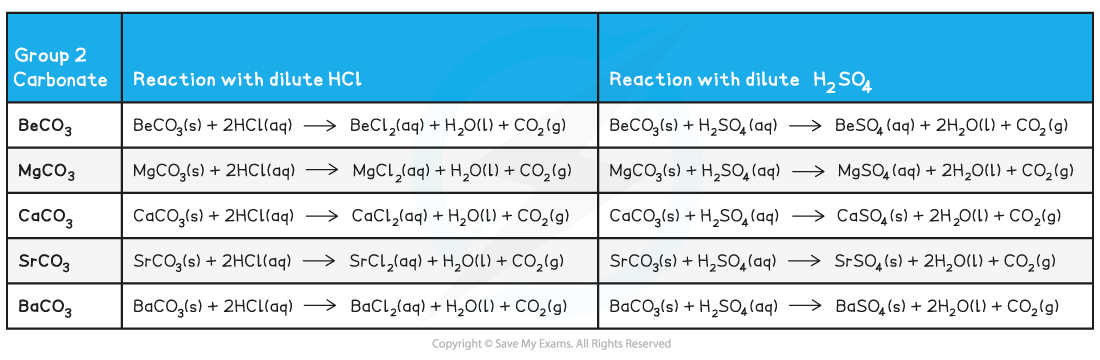
- Remember that:
carbonate + dilute hydrochloric acid → salt + water + carbon dioxide
carbonate + dilute sulfuric acid → sulfate + water + carbon dioxide
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









