- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
CIE A Level Biology復習筆記19.1.9 Gel Electrophoresis
Gel Electrophoresis
- Gel electrophoresis is a technique used widely in the analysis of DNA, RNA and proteins. During electrophoresis the?molecules?are?separated?according to their?size / mass?and their?net (overall) charge
- The separation occurs because:
- Of the electrical charge molecules carry – positively charged molecules will move towards the cathode (negative pole) whereas negatively charged molecules will move towards the anode (positive pole) eg.?DNA is negatively charged?due to the?phosphate?groups and thus when placed in an electric field the molecules?move towards the anode
- Different sized molecules move through the gel (agarose for DNA and polyacrylamide – PAG for proteins) at different rates. The tiny pores in the gel result in?smaller molecules?moving?quickly, whereas?larger molecules?move?slowly
- Of the type of gel – different gels have different sized pores which affects the speed the molecules can move through them
DNA separation
- DNA can be collected from almost anywhere on the body, e.g. the root of a hair or saliva from a cup. After collection DNA must be prepared for gel electrophoresis so that the?DNA?can be?sequenced?or analysed for?genetic profiling?(fingerprinting)
- To prepare the fragments scientists must first increase (amplify) the number of DNA molecules by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Then restriction endonucleases (enzymes) are used to cut the DNA into fragments
- Different restriction enzymes cut the DNA at different base sequences. Therefore scientists use enzymes that will cut close to the?variable number tandem repeat?(VNTR) regions
- Variable number tandem repeats?(VNTRs) are regions found in the non-coding part of DNA. They contain?variable numbers of repeated DNA sequences?and are known to?vary between different people?(except for identical twins). These VNTR may be referred to as ‘satellite’ or ‘microsatellite’ DNA
- To separate the DNA fragments in gel electrophoresis the scientists :
- Create an agarose gel plate in a tank. Wells (a series of groves) are cut into the gel at one end
- Submerge the gel in an electrolyte solution (a salt solution that conducts electricity) in the tank
- Load (insert) the fragments into the wells using a micropipette
- Apply an electrical current to the tank. The negative electrode must be connected to the end of the plate with the wells as the DNA fragments will then move towards the anode (positive pole) due to the attraction between the negatively charged phosphates of DNA and the anode
- The smaller mass / shorter pieces of DNA fragments will move faster and further from the wells than the larger fragments
- The fragments are not visible so must be transferred onto absorbent paper or nitrocellulose which is then heated to separate the two DNA strands.?Probes?are then added, after which an X-ray image is taken or UV-light is shone onto the paper producing a pattern of bands which is generally compared to a control fragment of DNA
- Probes?are?single-stranded DNA sequences?that are?complementary?to the?VNTR?regions sought by the scientists. The probes also contain a means by which to be identified. This can either be:
- A radioactive label (eg. a phosphorus isotope) which causes the probes to emit radiation that makes the X-ray film go dark, creating a pattern of dark bands
- A fluorescent stain / dye (eg. ethidium bromide) which fluoresces (shines) when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, creating a pattern of coloured bands
Protein separation
- The different amino acids (because of the different R groups) determine the charge of proteins. The charge of the R groups depends on the pH and therefore buffer solutions are used during the separation of proteins to keep the pH constant
- Gel electrophoresis is used to separate polypeptide chains produced by different alleles eg. the haemoglobin variants (α-globin, β-globin and the sickle cell anaemia variant of β-globin)
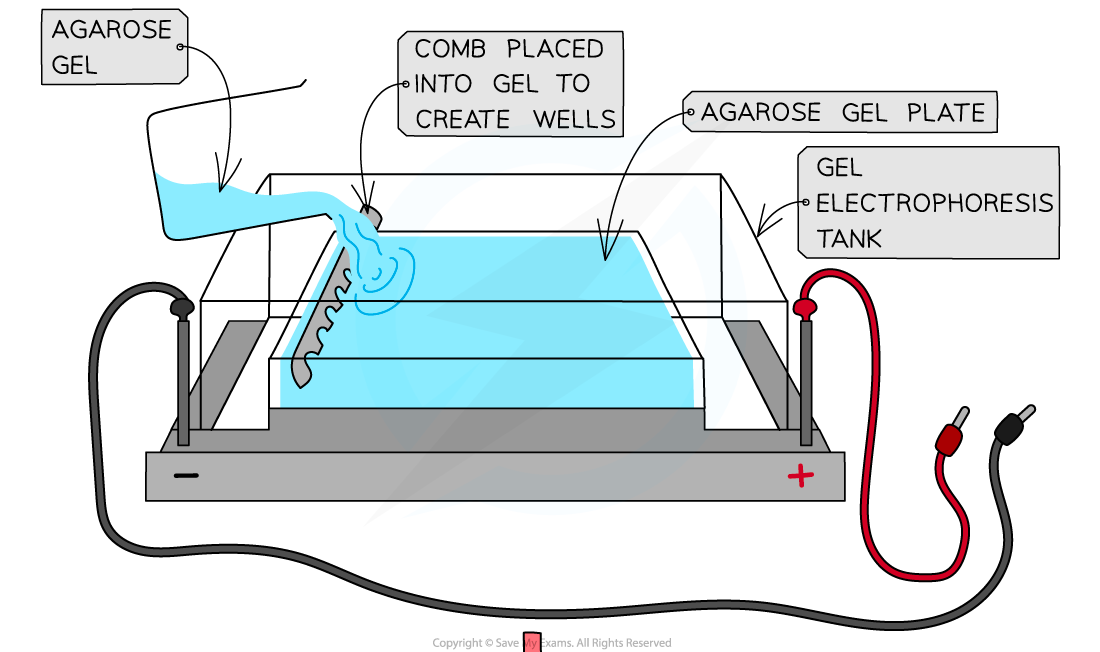
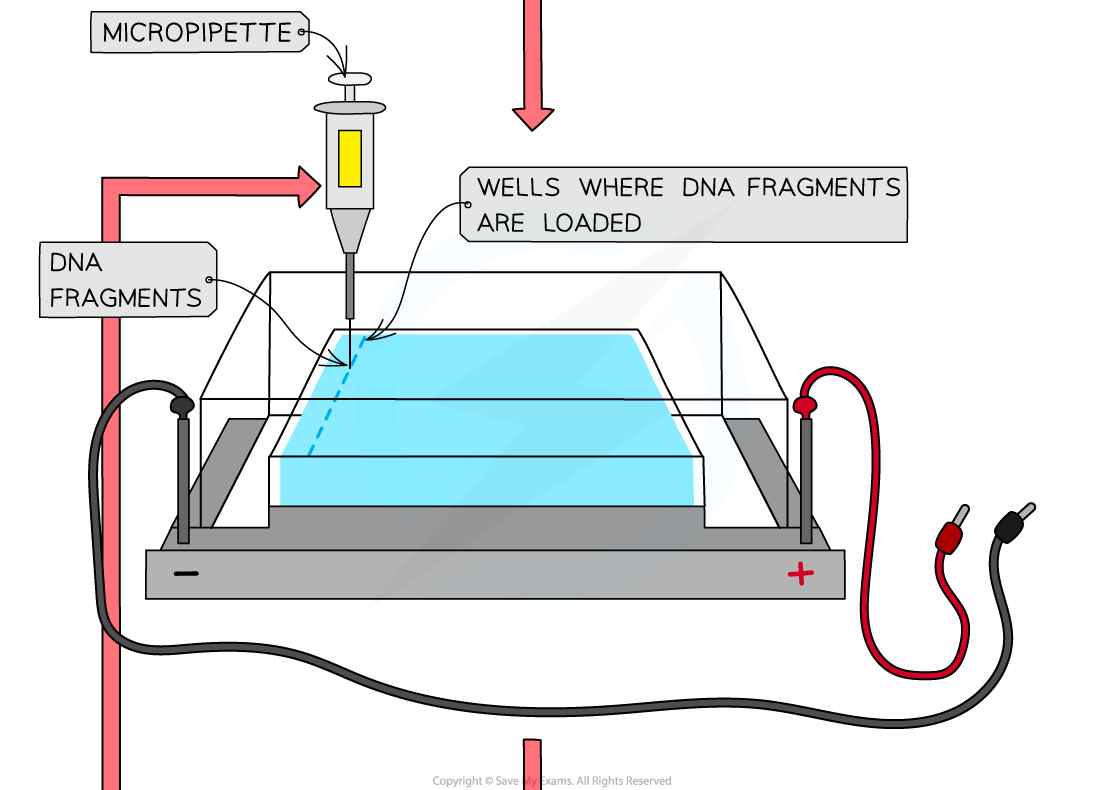
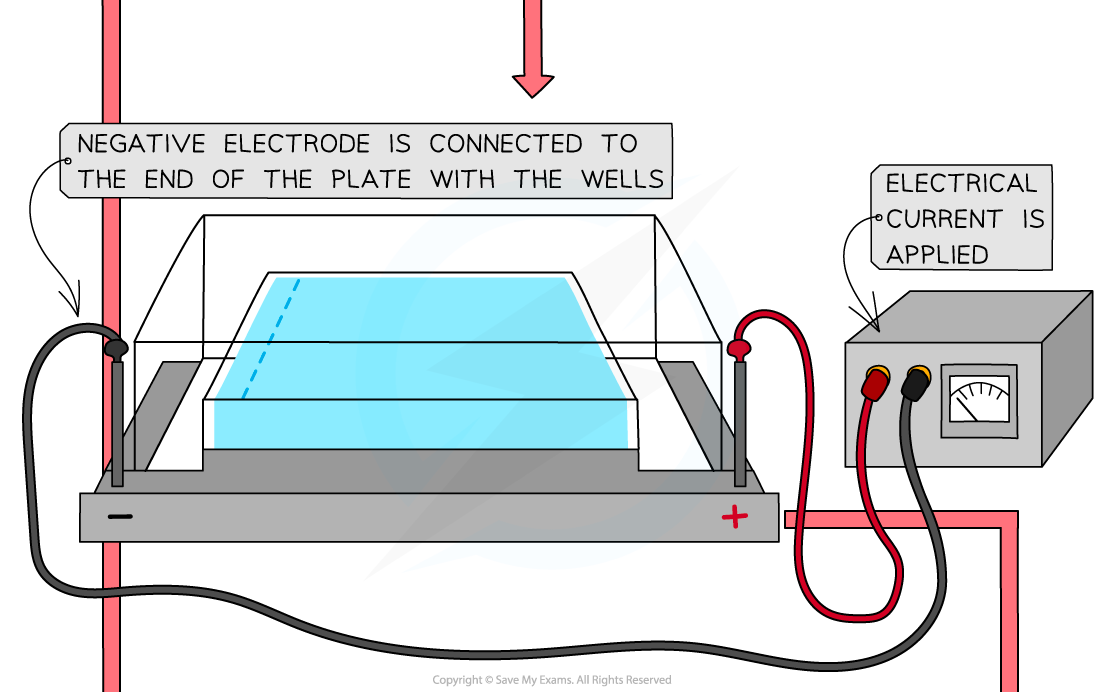
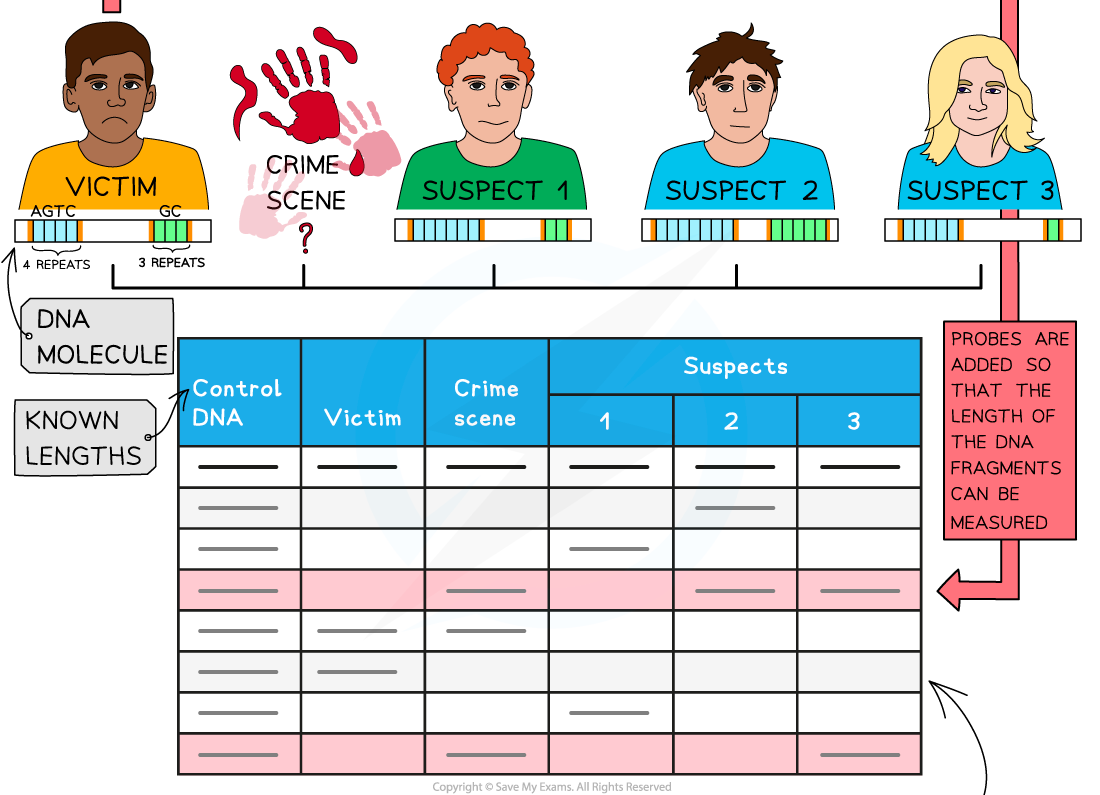
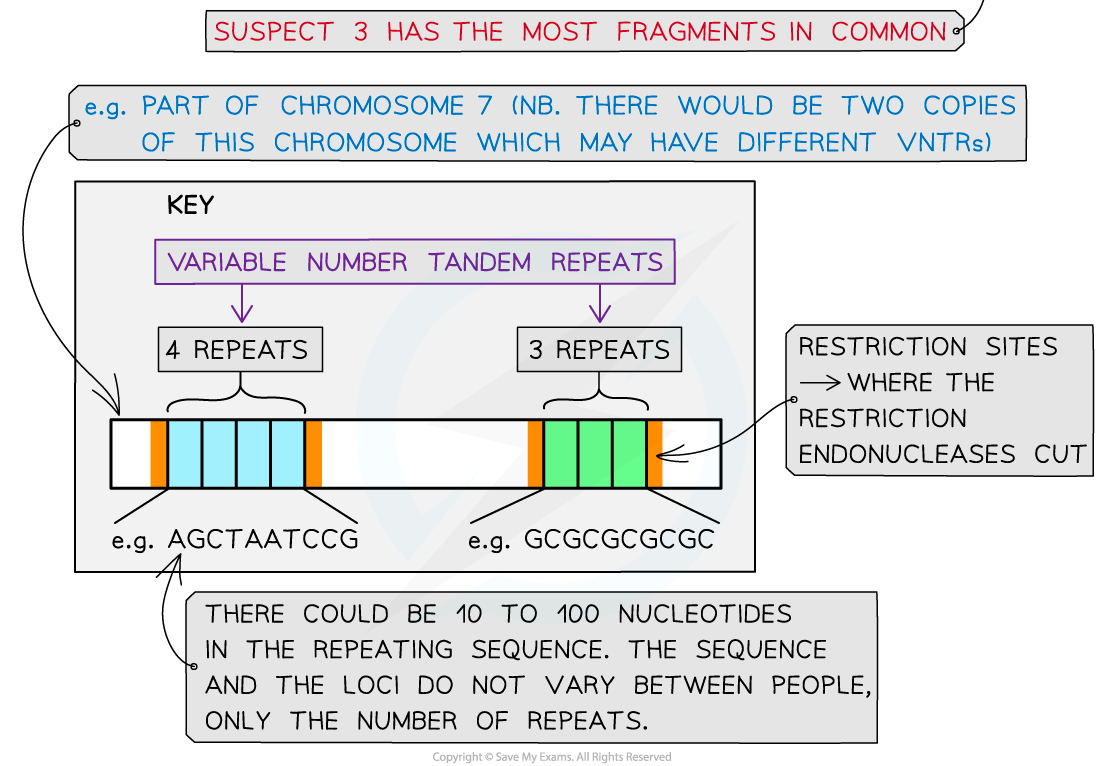
The separation of DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis. Gel electrophoresis can be used in DNA profiling where scientists separate the VNTRs (as these are unique to every person except identical twins)
Exam Tip
Remember gel electrophoresis is the separation of molecules according to their size and charge (negatively charged DNA molecules move to the positive pole). Examiners like to ask questions about gel electrophoresis.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









