- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動(dòng)、國際課程、科研項(xiàng)目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics復(fù)習(xí)筆記6.6.1 Gas Laws v Kinetic Theory
Gas Laws v Kinetic Theory
- There is a scientific distinction between the gas laws and kinetic theory
Gas Laws
- The gas laws are?empirical?in nature which means they are based on?observation?and?evidence
- The gas laws include Boyle's Law, Charles's Law, Pressure Law and the ideal gas equation
- These are all based on observations of how a gas responds to changes in its environment, namely volume, pressure and temperature from experiment
Kinetic Theory
- Kinetic theory is based on?theory?(as stated in its name)
- This means it is based on?assumptions?and?derivations?from existing theories
- These are then used to explain why the gas laws behave the way they do
Ideal Gas Internal Energy
- The?internal energy?of an object is intrinsically related to its?temperature
- When a container containing gas molecules is heated up, the molecules begin to?move around faster,?increasing their kinetic energy
- If the object is a solid, where the molecules are tightly packed, when heated the molecules begin to?vibrate?more
- Molecules in liquids and solids have both kinetic and potential energy because they are close together and bound by intermolecular forces
- However, ideal gas molecules are assumed to have?no intermolecular forces
- This means they have?no potential energy, only kinetic energy
- This means that the ideal gas internal energy is the?kinetic energy?of the atoms
- The (change in) internal energy of an ideal gas is equal to:
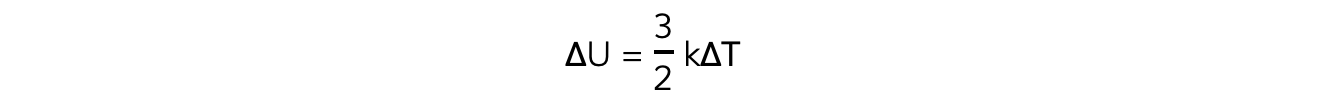
- Therefore, the change in internal energy is proportional to the change in temperature:
ΔU?∝ ΔT
- Where:
- ΔU?= change in internal energy (J)
- ΔT?= change in temperature (K)
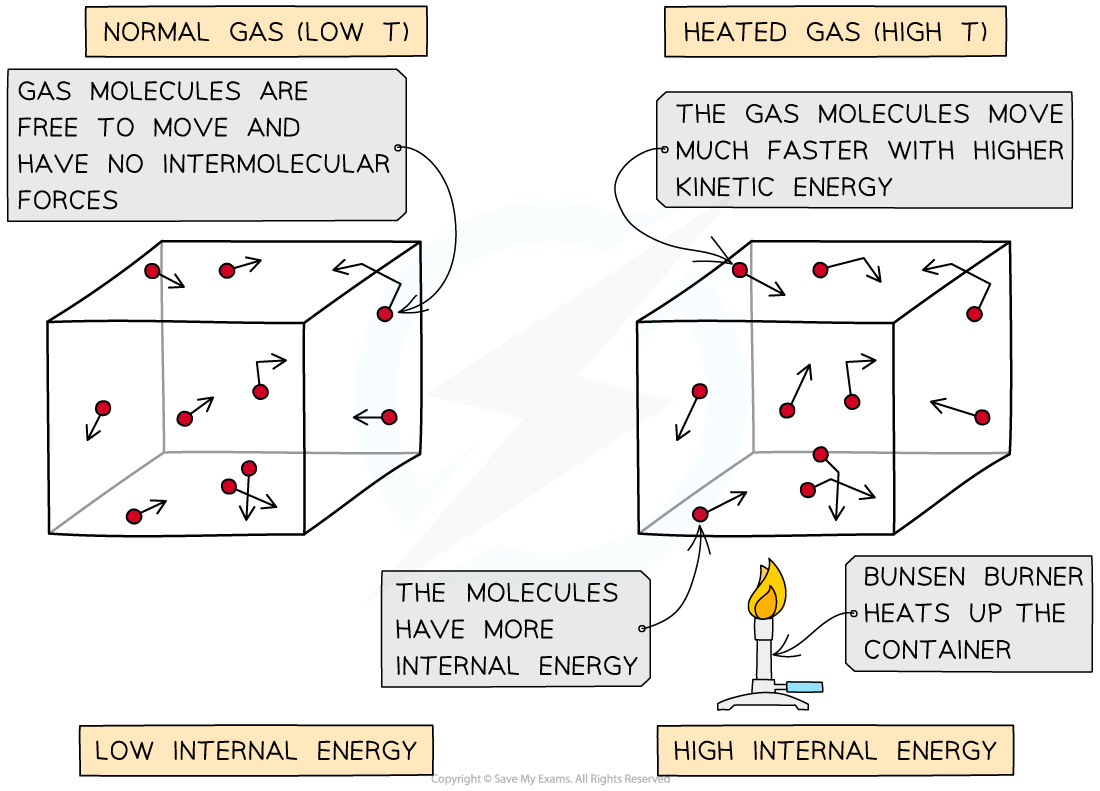
As the container is heated up, the gas molecules move faster with higher kinetic energy and therefore higher internal energy
Worked Example
A student suggests that when an ideal gas is heated from 50 °C to 150 °C, the internal energy of the gas is trebled.State and explain whether the student's suggestion is correct.
Step 1: Write down the relationship between internal energy and temperature
-
- The internal energy of an ideal gas is directly proportional to its temperature
ΔU?∝?ΔT
Step 2: Determine whether the change in temperature (in K) increases by three times
-
- The temperature change is the?thermodynamic?temperature ie. Kelvin
- The temperature change in degrees from 50 °C to 150 °C increases by three times
- The temperature change in Kelvin is:
50 °C?+ 273.15 = 323.15 K
150 °C?+ 273.15 = 423.15 K
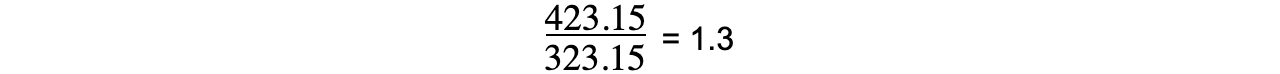
-
- Therefore, the temperature change, in Kelvin, does?not increase by three times
Step 3: Write a concluding statement relating the temperature change to the internal energy
-
- The internal energy is directly proportional to the temperature
- The thermodynamic temperature has not trebled, therefore, neither has the internal energy
- Therefore, the student is incorrect
Exam Tip
If an exam question about an ideal gas asks for the?total internal energy, remember that this is equal to the?total kinetic energy?since an ideal gas has?zero potential energy
轉(zhuǎn)載自savemyexams

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









