- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry復習筆記1.8.2 Le Chatelier's principle
Le Chatelier's Principle
Position of the equilibrium
- The?position of the equilibrium?refers to the relative amounts of products and reactants in an equilibrium mixture
- When the position of equilibrium shifts to the?left, it means the concentration of?reactants?increases
- When the position of equilibrium shifts to the?right, it means the concentration of?products?increases
Le Chatelier’s principle
- Le Chatelier’s principle?says that if a change is made to a system in dynamic equilibrium, the position of the equilibrium moves to counteract this change
- The principle is used to predict changes to the position of equilibrium when there are changes in temperature, pressure or concentration
Effects of concentration
- How the equilbrium shifts with concentration changes:

Worked Example
Changes in equilibrium positionUsing the reaction below:
CH3COOH (I) + C2H5OH (I)???? CH3COOC2H5?(I) + H2O (I)
Explain what happens to the position of equilibrium when:
- More?CH3COOC2H5?is added
- Some C2H5OH is removed
Using the reaction below:
Ce4+?(aq) + Fe2+?(aq)???Ce3+?(aq)?+ Fe3+?(aq)
Explain what happens to the position of equilibrium when
- Water is added to the equilibrium mixture
Answer 1:
-
- The position of the equilibrium moves to the left and more ethanoic acid and ethanol are formed.
- The reaction moves in this direction to oppose the effect of added ethyl ethanoate, so the ethyl ethanoate decreases in concentration.
Answer 2:
-
- The position of the equilibrium moves to the left and more ethanoic acid and ethanol are formed.
- The reaction moves in this direction to oppose the removal of ethanol so more ethanol (and ethanoic acid) are formed from ethyl ethanoate and water.
Answer 3:
-
- There is no effect as the water dilutes all the ions equally so there is no change in the ratio of reactants to products.
Effects of pressure
- Changes in pressure only affect reactions where the reactants or products are gases
- How the equilibrium shifts with pressure changes:

Worked Example
Changes in pressurePredict the effect of increasing the pressure on the following reactions:
- N2O4?(g)???2NO2?(g)
- CaCO3?(s)???CaO (s) + CO2?(g)
Predict the effect of decreasing the pressure on the following reaction:
- 2NO2?(g)???2NO (g) + O2?(g)
Answer 1:
-
- The equilibrium shifts to the left as there are fewer gas molecules on the left
- This causes a decrease in pressure
Answer 2:
-
- The equilibrium shifts to the left as there are no gas molecules on the left but there is CO2?on the right
- This causes a decrease in pressure
Answer 3:
-
- The equilibrium shifts to the right as there is a greater number of gas molecules on the right
- This causes an increase in pressure
Effects of temperature
- How the equilbrium shifts with temperature changes:
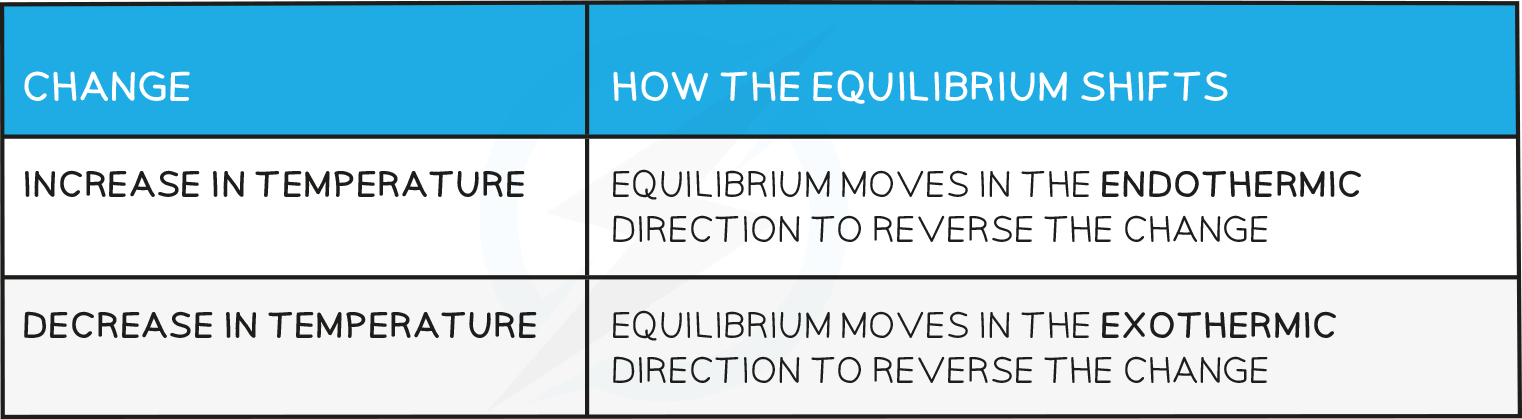
Worked Example
Changes in temperatureUsing the reaction below:
H2?(g) + CO2?(g)??? H2O (g) + CO (g)? ? ΔH = +41.2 kJ mol-1
- Predict the effect of increasing the temperature on this reaction
Using the reaction below:
Ag2CO3?(s)???? Ag2O (s) + CO2?(g)
- Increasing the temperature increases the amount of CO2(g) at constant pressure. Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic?
Explain your answer
Answer 1:
-
- The reaction will absorb the excess energy and since the forward reaction is endothermic, the equilibrium will shift to the right.
Answer 2:
-
- The reaction will absorb the excess energy and since this causes a shift of the equilibrium towards the right (as more CO2(g) is formed) this means that the reaction is endothermic.
Effects of catalysts
- A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction (they increase the rate of the?forward?and?reverse?reaction?equally)
- Catalysts only cause a reaction to reach equilibrium?faster
- Catalysts therefore have?no effect?on the?position of the equilibrium?once this is reached
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









