- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動(dòng)、國際課程、科研項(xiàng)目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry復(fù)習(xí)筆記1.4.10 Effects of Structure & Bonding
Effects of Bonding & Structure on Physical Properties
- Different types of?structure?and?bonding?have different effects on the?physical properties?of substances such as their?melting?and?boiling points,?electrical conductivity?and?solubility
Ionic bonding & giant ionic lattice structures
- Ionic compounds are?strong
- The?strong electrostatic forces?in ionic compounds keep the ions strongly together
- They are?brittle?(meaning ionic crystals can split apart easily)
- Ionic compounds have?high melting?and?boiling?points
- The strong electrostatic forces between the ions in the lattice act in all directions and keep them strongly together
- Melting and boiling points increase with charge density of the ions due to the greater?electrostatic attraction?of charges
- For example, Mg2+O2-?has a higher melting point than Na+Cl-
- Ionic compounds are?soluble?in water as they can form?ion - dipole bonds
- Ionic compounds only?conduct?electricity?when?molten?or in?solution
- When molten or in solution, the ions can freely move around and conduct electricity
- In the solid state they’re in a fixed position and unable to move around
Metallic bonding & giant metallic lattice structures
- Metallic structures are?malleable
- When a force is applied, the metal layers can slide
- The?attractive forces?between the metal ions and electrons act in all directions
- So when the layers slide, the metallic bonds are re-formed
- The lattice is not broken and has changed shape
- Metallic lattices are?strong?and?hard
- Due to the strong attractive forces between the metal ions and delocalised electrons
- Metals have?high melting?and?boiling points
- Pure metals?are?insoluble?in water
- Metals can?conduct electricity?when in the?solid?or?liquid?state
- As both in the solid and liquid state there are?mobile electrons?which can freely move around and conduct electricity
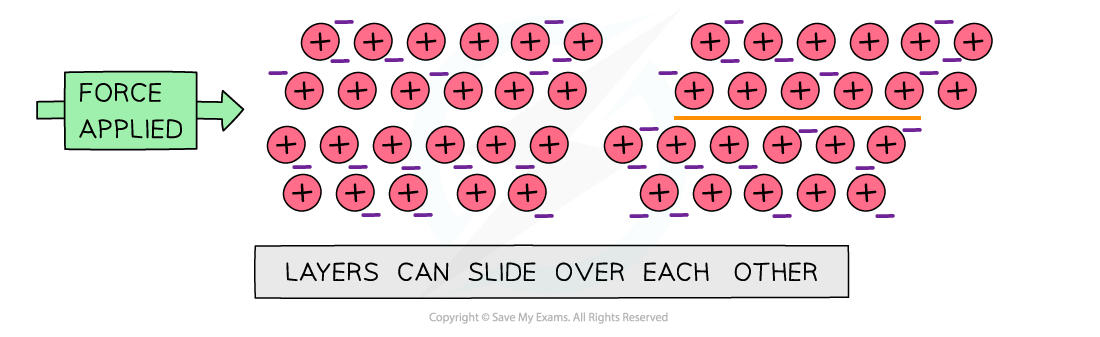
Metals are malleable as the layers can slide over each without breaking the attraction
Covalent bonding & simple covalent lattice structures
- Simple covalent lattices?have low?melting?and?boiling points
- These compounds have weak intermolecular forces between the molecules
- Only little energy is required to break the lattice
- Most compounds are insoluble with water
- Unless they are polar and can form hydrogen bonds?(such as sucrose)
- They do not?conduct electricity?in the?solid?or?liquid?state as there are no charged particles
- Some simple covalent compounds do conduct electricity in solution, but this is a reaction with the water than produces ions such as HCl which forms H+?and Cl-?ions
Covalent bonding & giant covalent lattice structures
- Giant covalent lattices?have?very high?melting?and?boiling points
- These compounds have a large number of?covalent bonds?linking the whole structure
- A lot of energy is required to break the lattice
- The compounds can be?hard?or?soft
- Graphite is?soft?as the forces between the carbon layers are weak
- Diamond and silicon(IV) oxide are?hard?as it is difficult to break their 3D network of strong covalent bonds
- Most compounds are insoluble with water
- Most compounds do not?conduct electricity?however some do
- Graphite has?delocalised?electrons between the carbon layers which can move along the layers when a voltage is applied
- Diamond and silicon(IV) oxide do not conduct electricity as all four outer electrons on every carbon atom are involved in a?covalent bond?so there are no freely moving electrons available
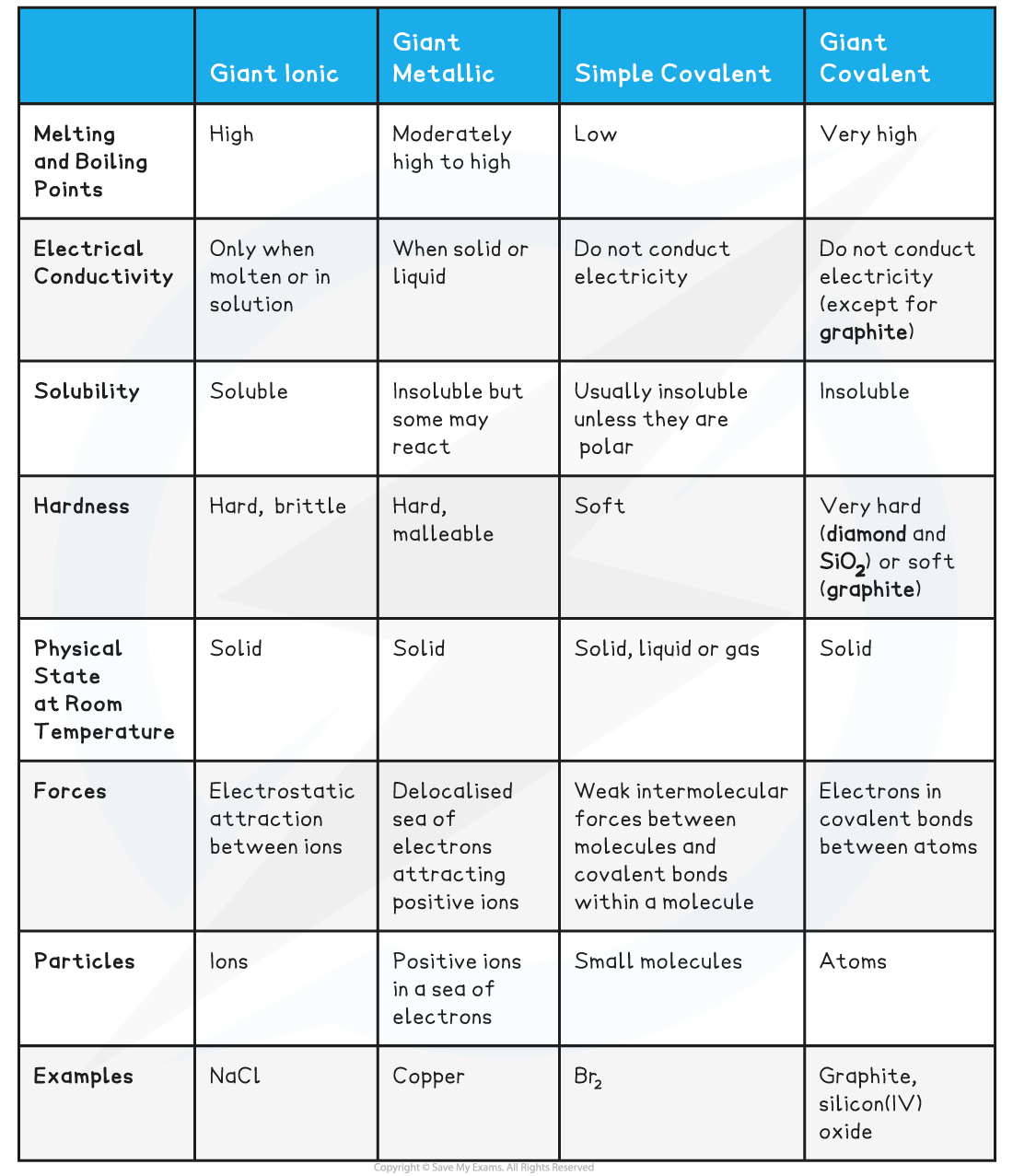
Characteristics of Different Compound Structure Types Table
Worked Example
Bonding & structureThe table below shows the physical properties of substances X, Y and Z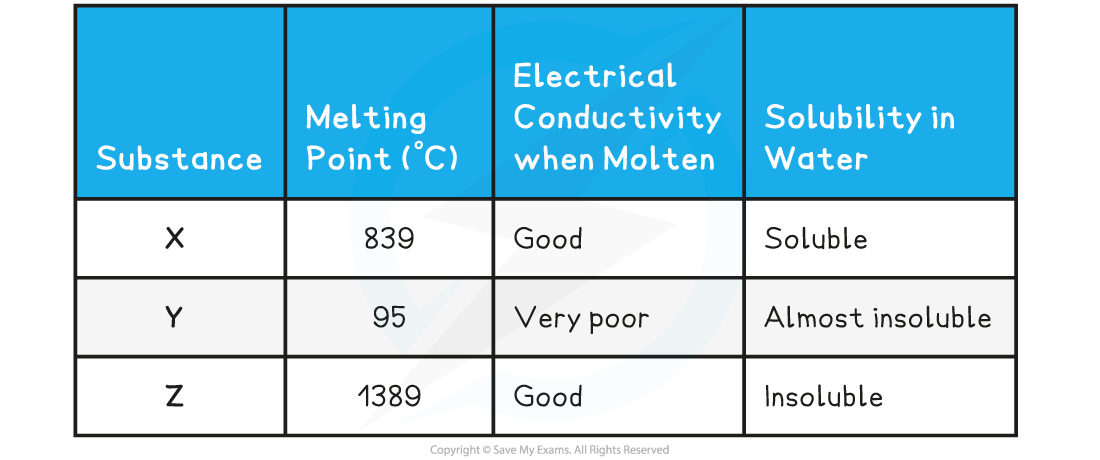 Which one of the following statements about X and Y is completely true?Statement 1:?X has a giant ionic structure, Y has a giant molecular structure, Z is a metalStatement 2:?X is a metal, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z has a giant molecular structureStatement 3:?X is a metal, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z has a giant ionic structureStatement 4:?X has a giant ionic structure, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z is a metal
Which one of the following statements about X and Y is completely true?Statement 1:?X has a giant ionic structure, Y has a giant molecular structure, Z is a metalStatement 2:?X is a metal, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z has a giant molecular structureStatement 3:?X is a metal, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z has a giant ionic structureStatement 4:?X has a giant ionic structure, Y has a simple molecular structure, Z is a metal
Answer
The correct answer is?Statement 4
-
- The relatively high melting point, solubility in water and electrical conductivity when molten suggest that?X?is a?giant ionic structure.
- The low melting point of?Y?suggests that little energy is needed to break the lattice which corresponds to a?simple molecular structure. This is further supported by the low electrical conductivity and its being almost insoluble in water.
- Compound?Z?has a very high melting point which is characteristic of either metallic or giant molecular lattices, however since it conducts electricity, compound Z must be a?giant metallic lattice.
轉(zhuǎn)載自savemyexams

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號(hào)-1









