- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Chemistry復習筆記7.7.1 Amino Acids
Amino Acids
- Amino acids?are?organic compounds?that contain two functional groups:
- A basic?amino?(-NH2) group
- An acidic?carboxylic?acid?(-COOH) group
- Due to the presence of both a?basic?and?acidic?group in amino acids, they are said to be?amphoteric
- They can act as both acids and bases
Naturally occurring amino acids
- 2-aminocarboxylic acids?are a type of amino acids in which the amine (-NH2) group is bonded to the carbon atom?next?to the -COOH group
- These type of amino acids form the ‘building blocks’ that make up?proteins
- There are?20?naturally occurring amino acids with the general structural formula of?RCH(NH2)COOH
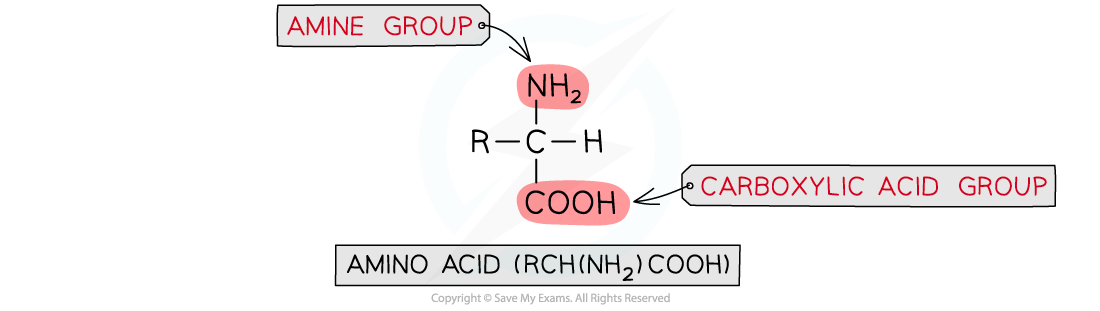
General structural formula of amino acids
- The?R?group varies in different amino acids and can be:
- Acidic
- Basic
- Neutral
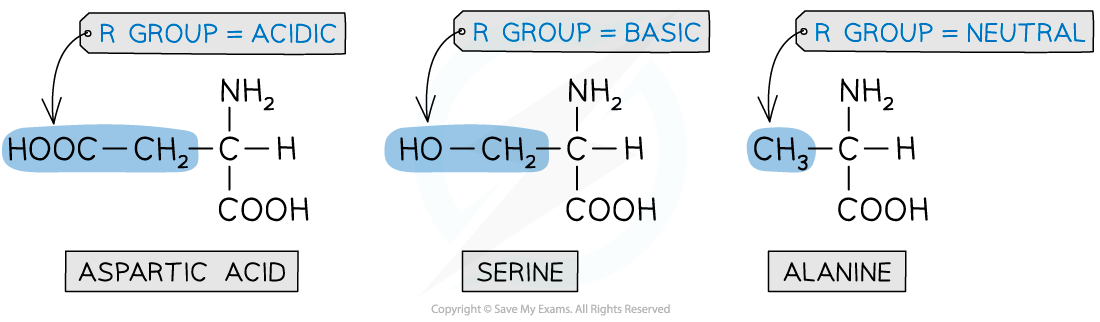
The R group varies in different amino acids
Acid / base properties of amino acids
- Amino acids will undergo most reactions of amines and carboxylic acids including acid-base reactions of:
- Amines with acids
- Carboxylic acids with bases
- However, they can also interact?intramolecularly?(within themselves) to form a?zwitterion
- A zwitterion is an ion with both a?positive?(-NH3+) and a?negative?(-COO-) charge
- Because of these charges in a zwitterion, there are?strong intermolecular forces of attraction?between amino acids
- Amino acids are therefore?soluble crystalline solids

An amino acid molecule can interact within itself to form a zwitterion
Isoelectric point
- A solution of amino acids in water will exist as?zwitterions?with both?acidic?and?basic?properties
- They act as?buffer solutions?as they resist any changes in pH when?small?amounts of acids or alkali are added
- If an acid is added (and thus the pH is?lowered):
- The -COO-?part of the zwitterion will?accept?an H+?ion to reform the -COOH group
- This causes the zwitterion to become a?positively charged ion
- If a base is added (and thus the pH is?raised):
- The -NH3+?part of the zwitterion will?donate?an H+?ion to reform the -NH2?group
- This causes the zwitterion to become a?negatively charged ion
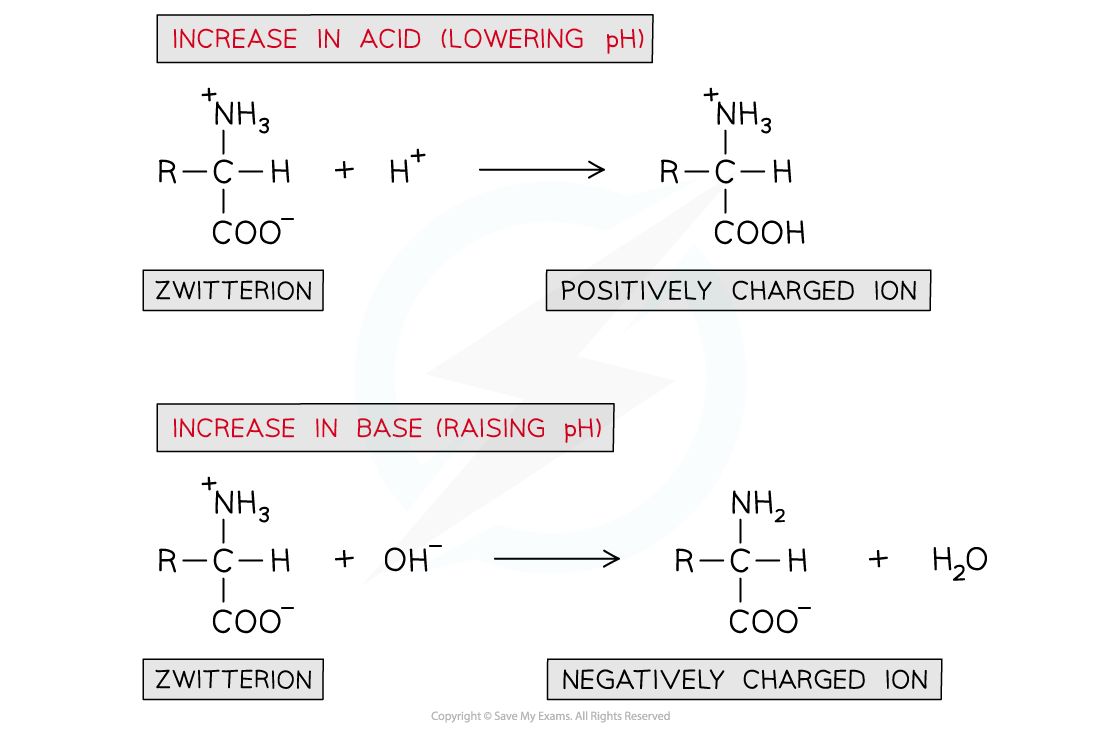
A solution of amino acids can act as a buffer solution by resisting any small changes in pH
- The pH can be slightly adjusted to reach a point at which neither the?negatively charged?or?positively charged?ions dominate and the amino acid exists as a?neutral zwitterion
- This is called the?isoelectric point?of the amino acid
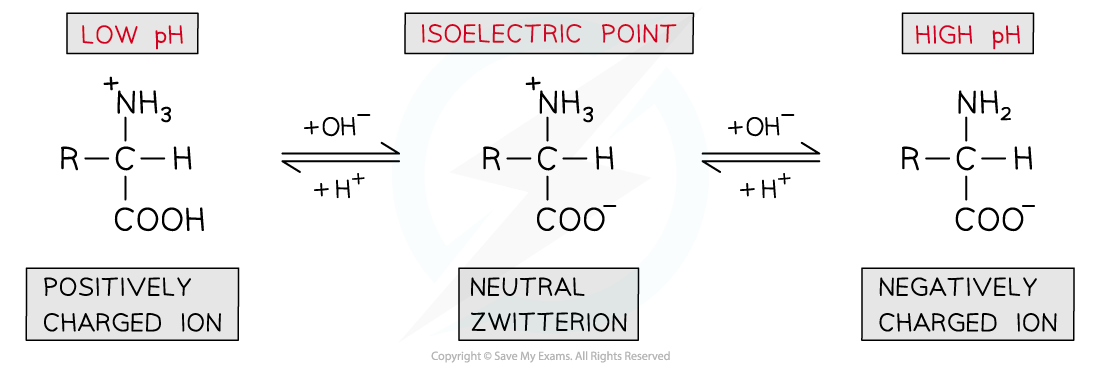
The isoelectric point of amino acids is the pH at which the amino acid exists as a neutral zwitterion
Exam Tip
Naturally occurring amino acids are usually referred to by a traditional name and a three letter code as the IUPAC systematic names can be rather complicated. For example, aspartic acid, serine and alanine are abbreviated to Asp, Ser and Ala, respectively.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









