- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
藤校學霸們都參加的美國四大數學頂尖夏校!
參加的學生中67%都進入哈耶普斯麻,想要get藤校錄取學霸的同款活動嗎?今天翰林就為大家來詳細介紹一下四大數學夏校!感興趣的同學們趕緊收藏收藏!
ROSS數學營
Ross Mathematics Program
ROSS于1957年在圣母大學創立,并于1964年起與俄亥俄州立大學聯合舉辦,是美國三大數學營(另外兩個是PROYMS,斯坦福數學營)之首,在數學圈內名聲極大。
ROSS數學營每年只接受40名第一年參與的學生以及10-15名青年輔導員(junior counselors)。其中青年輔導員是上一年在項目中表現優異,想重返參加的學生。
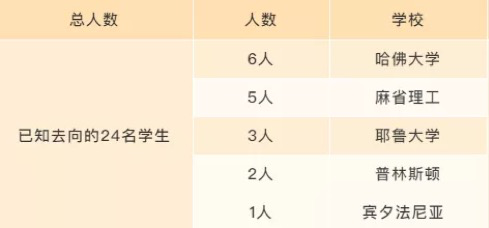
ROSS數學營學員的大學申請成績極為亮麗,以上是24名已知去向的參加,其他7位學生分別選擇杜克大學、UC伯克利大學、滑鐵盧大學、密歇根大學、東北大學、亞利桑那州立大學等等。
由于疫情影響,2020和2021年ROSS數學營都采用了線上模式進行,2022年預計為線上形式(以官方具體通知為準)。
適合學生:全球15-18歲學生
申請時間:1月開放申請窗口,4月1日截止。招生委員會將于3月開始做出錄取決定。
開營時間:6月27日-8月6日共六周(參考2021年)
申請要求:申請表、簡答題、數論題、學校成績單、教師推薦信、托福不低于80分且口語22分以上。
數學測試題的特點:Ross數學測試有4道提供,每道題又包含很多小問題。注重引導申請者發現規律。小題目由淺入深,理論知識越來越難,需要總結的規律層次也越深。羅斯題目很開放,沒有固定答案,在做題過程中可以得出很多結論,申請者需要證明自己的結論,不論正取與否。
Ross數學營的申請難度極大,招生比例不超過10%。Ross美國營每年只招60位新學員,中國學生的錄取率則更低。所以充足的準備,是一定不能少的,畢竟進入Ross數學營相當于半只腳已經踏入了常春藤名校!
課程費用:$1500
課程內容:以數論為中心延伸至以下方向:歐幾里德算法、模塊化算術、多項式、二項式系數、連續分數、高斯整數、數學幾何、有限域等。課程為期6周,每周上課8小時(講座5小時,問題研討會3小時)。除此之外,還需要劃分時間去解決課程上的數學遺留問題,每解決一個數學問題后,需要寫一份清晰完整的證明過程。
課程大致主題:
Euclid’s Algorithm.
Greatest common divisor. Diophantine equation ax + by = c.
Proof of unique factorization in Z.
Modular arithmetic.
Inverses. Solving congruences. Fermat’s Theorem. Chinese Remainder Theorem.
Hensel’s lemma for solving congruences (mod pm).
Binomial coefficients.
Pascal’s triangle. Binomial Theorem.
Arithmetic properties of binomial coefficients, like: (x+y)p = xp + yp (mod p).
Polynomials.
Division algorithm, Remainder Theorem, number of roots.
Polynomials in Zp[x]. Irreducibles and unique factorization.
Z[x] and Gauss’s Lemma.
Cyclotomic polynomials.
Orders of elements.
Units. The group Um. Computing orders.
Cyclicity of Up. For which m is Um cyclic?
Quadratic reciprocity.
Legendre symbols. Euler’s criterion. Gauss’s fourth proof of Reciprocity.
Jacobi symbols.
Continued fractions.
Computing convergents. |x – p/q| < 1/q2.
Best rational approximations. Pell’s equation.
Arithmetic functions.
phi(n), tau(n), sigma(n), and mu(n). Multiplicative functions.
Sum of f(d) as d divides n. Moebius Inversion.
Convolutions of functions.
Gaussian integers: Z[i].
Norms. Which rational primes have Gaussian factors? Division algorithm.
Unique factorization. Fermat’s two squares theorem.
Counting residues (mod a+bi).
Finite fields.
Characteristic. Frobenius map. Factoring xpn – x.
Counting irreducible polynomials.
Uniqueness Theorem for the field of pn elements.
Resultants.
Discriminant of a polynomial and formal derivatives.
Resultant of two polynomials and relation with Euclid’s algorithm.
Another proof of Quadratic Reciprocity.
Geometry of numbers.
Lattice points. Pick’s Theorem. Minkowski’s Theorem.
Geometric interpretation of the Farey sequence and continued fractions.
Geometric proofs of the two square and four square theorems.
Quadratic number fields.
Which quadratic number rings are Euclidean? For instance
Z[sqrt(d)] is Euclidean when d = -1, -2, 2, 3 but not when d = -3, -5 or 5.
Algebraic integers.
SUMaC斯坦福大學數學營
Stanford University Mathematics Camp
SUMaC成立于1995年,由斯坦福大學三位教授合作創立和運營。每年招收40名學生,目前參與者已遍布50多個國家和地區,是北美地區影響力非常大的數學項目制夏校之一。斯坦福大學數學營(SUMaC)通過課程,指導性研究和小組問題解決引領學員進入高等數學之旅。在以數學為中心的活動環境中,探索數學研究的趨勢,回顧重要數學領域的歷史發展以及跨科學學科的應用。
項目特點:SUMaC課程的重點純粹是研究數學這門獨立的學科,并在學習的過程中引進各重要的應用等。但是SUMaC課程并不是為了學分或成績而設計的,純粹是為了提高分享數學的魅力。在這樣的目標為前提下,SUMaC為學生提供兩個研究方向的主題課程作為選擇,學生可以任選其中之一,深入地研究自己感興趣的課題而不必過多擔心自己的成績。20多年來,這已經成為了SUMaC得以吸引眾多學生的亮點之一。
SUMaC項目專注于純數學,同時提供高度挑戰性的Program I和Program II兩個系列課程。今年Program I的主題是抽象代數和數論,研究方向包括Cryptography, Constructibility, Coding Theory, and Symmetry。Program II的主題是代數拓撲學。兩個系列都是當前數學研究的核心主題,同學們只能選擇其中一個方向深入學習。
Program I-抽象代數與數論:該課程將通過5個問題進行開展,包括直尺和羅盤構造的局限性,二維模式的分類,糾錯碼,密碼學以及結構對稱性分
Program II-代數拓撲:該課程重點是代數拓撲,拓撲是對不受變形影響的形狀特性的研究,這是當前數學研究的主要領域。本課程將探索使用代數概念(例如群的概念)分析形狀的拓撲特性的不同方法。
由于疫情影響,2021年SUMaC轉為在線舉行,2022年預計為線上形式。
適合學生:全球10-11年級學生
申請時間:1月開放申請,3月10日截止(參考2021年)
開營時間:共2期,每期3周(參考2021年)
第一期:6月21日-7月9日
第二期:7月19日-8月6日
適合學生:全球15-18歲學生
申請要求:學校成績單、教師推薦信、數學作業樣本、入營考試題、學生陳述的入營理由、財政資助申請表(按照學生個人需求*)等。
PROMYS青少年科學家數學項目
Program?in?Mathematics?for Young?Scientists
青年科學家數學計劃Program in Mathematics for Young Scientists,簡稱PROMYS,于1989年由格倫?史蒂文斯教授和其他三位現任教職員工創立。它與羅斯數學訓練營(Ross Mathematics Program)和斯坦福數學夏令營(Stanford University Mathematics Camp)并稱為美國三大頂尖數學訓練營。
PROMYS旨在鼓勵有理想、有抱負的中學生探索充滿創造力的數學世界。每年有來自世界各地的約80名中學生(60名新生及20名老生),在波士頓大學校園里進行數學探索項目。作為同樣以研究數論為主的訓練營,他們有著相似的教學模式,但是也有細節上的區別,感興趣的同學、家長可以深入了解,選擇更適合自己的項目。
適合學生:14-18周歲,完成9年級學習的中學生
申請時間:1月開放申請(參考2021年)
開營時間:7月3日-8月13日(參考2021年)
地點:波士頓大學,線下(初步計劃)
申請要求:學校成績、教師推薦信、入營考試題、文書、申請表等。
注:PROMYS的申請材料中不包含托福成績,但是營期所有講座、交流都是全英文的,所以一定要英文過關才能參加。測試題是申請材料中最重要的部分,雖然不一定要全部答出來,但是從測試題中,招生人員能看出你的思維過程,如何面對有挑戰性的問題等,一定要認真對待。
美加數學營
Canada/USA Mathcamp
美加數學營成立于1993年,是美國數學基金會的旗艦項目,Canada/USA Mathcamp是一個針對高中數學天才進行為期5周的暑期強化課程,課程內容均是大學數學甚至是研究生水平的數學主題課程,和數學學術活動沒有直接關聯,旨在使學生接觸高級數學思想和新的思維方式。數學營面向全球13至18歲且具有很高數學水平和興趣的中學生,其中不乏入選各國國家奧數集訓隊的學生。
Mathcamp不僅僅是一個夏校,更是一個充滿活力的社區,由各種各樣的人組成,他們對學習和數學有著共同的熱愛。在Mathcamp,學生可以探索本科,甚至研究生課程,同時建立解決問題的能力,以幫助他們想要研究的任何領域。美加數學營每年大概招手120名學員(新生65人,老學員55人),提供的國際生名額比例在10%-15%。值得一提的是,Canada/USA Math Camp非常鼓勵和支持喜歡數學的女孩子申請。每年學員中,女生占比達到45%-50%,這無疑對女孩子有很大的吸引力。
由于疫情影響,2022年為線上形式舉辦。
適合學生:全球13-18歲學生
申請時間:1月開放申請,3月10日截止(參考2021年)
開營時間:7月3日-8月8日(參考2021年)
申請要求:學校信息及數學背景、2封推薦信(數學推薦信、個人推薦信)、申請測驗(5-10題)、申請文書。
Camp往年教授的數學科目:
Discrete Mathematics
Combinatorics (enumerative, algebraic, geometric)
Generating functions and partitions
Graph theory
Ramsey theory
Probability
Finite geometries
Polytopes and polyhedra
Combinatorial Game Theory
Algebra and Number Theory
Linear algebra
Groups, rings, and fields
Primes and factorization algorithms
Congruences and quadratic reciprocity
Galois theory
Algebraic number theory
Analytic number theory
Fermat's Last Theorem for polynomials
p-adic numbers
Geometry of numbers
Geometry and Topology
Euclidean and non-Euclidean (hyperbolic, spherical, projective, inversive) geometries
Geometric transformations
Algebraic geometry
Point-set topology
Combinatorial topology
Knot theory
The Brouwer Fixed-Point Theorem
Calculus and Analysis
Topics in calculus
Fourier analysis
Complex analysis
Real analysis
Dynamical systems
Set Theory, Logic, and Foundations
Cardinals and ordinals
G?del's Incompleteness Theorem
The Banach-Tarski Paradox
Model Theory
Category Theory
Computer Science
Theoretical CS
Complexity theory
Information Theory
Cryptography
Algorithms
Connections to Other Fields
Relativity and quantum mechanics
Neural networks
Mathematical biology
Game theory
Voting theory
Bayesian statistics
Discussions
Philosophy of Mathematics
Math Education
How to Give a Math Talk
College And Beyond
Problem Solving
Proof methods
Elementary and advanced techniques
Contest problems of various levels of difficulty
Relays and team competitions

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









